Understanding the Significance of 36 and 43.3 in Data Analysis

<!DOCTYPE html>
In the world of data analysis, certain numbers carry significant weight, and 36 and 43.3 are no exceptions. These values often appear in statistical calculations, machine learning models, and data visualization, making them crucial for professionals and enthusiasts alike. Understanding their significance can enhance your analytical skills and decision-making processes. Let’s dive into why these numbers matter and how they can be applied in real-world scenarios, (data analysis techniques, statistical significance, machine learning metrics)
The Role of 36 in Data Analysis

The number 36 frequently appears in statistical analysis, particularly in degrees of freedom calculations. Degrees of freedom are essential in hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and variance estimation. For instance, in a t-distribution, the degrees of freedom are often denoted as df = n - 1, where n is the sample size. If a sample size is 37, the degrees of freedom would be 36, influencing the critical values and p-values in statistical tests. (degrees of freedom, hypothesis testing, statistical calculations)
Key Applications of 36
- t-tests: Determines critical values for small sample sizes.
- ANOVA: Influences F-statistics in analysis of variance.
- Chi-square tests: Affects the distribution for categorical data analysis.
📊 Note: Always verify the degrees of freedom in your calculations to ensure accurate statistical inferences.
The Importance of 43.3 in Data Analysis

The number 43.3 might seem arbitrary, but it often emerges in machine learning metrics and data scaling. For example, in a dataset where values are normalized, 43.3 could represent a critical threshold or an outlier. Additionally, in regression analysis, a coefficient of 43.3 might indicate a strong relationship between variables, depending on the context. (machine learning metrics, data normalization, regression analysis)
Practical Uses of 43.3
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Outlier Detection | Identifying values like 43.3 that deviate significantly from the norm. |
| Threshold Setting | Using 43.3 as a benchmark in classification models. |
| Coefficient Analysis | Interpreting regression coefficients near 43.3 for variable impact. |
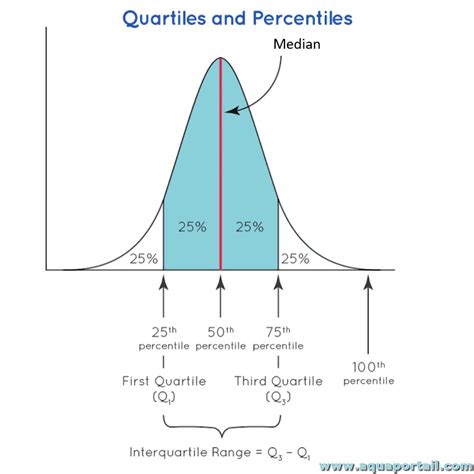
🔍 Note: Context is key when interpreting numbers like 43.3 in data analysis.
Combining 36 and 43.3 in Real-World Scenarios
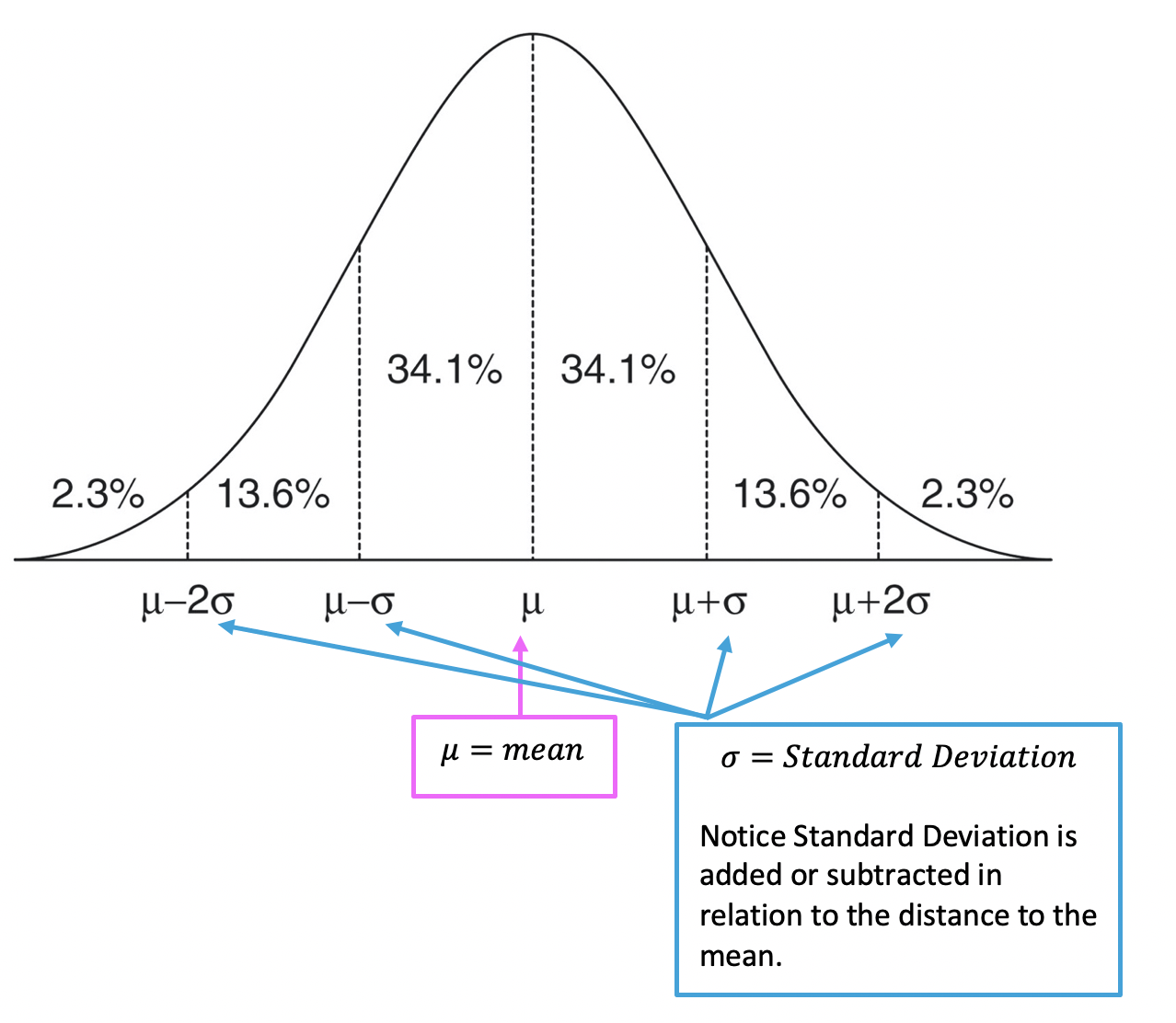
While 36 and 43.3 may seem unrelated, they can intersect in complex analyses. For instance, in a study with a sample size of 37, the degrees of freedom (36) might influence the significance of a regression coefficient (43.3). Understanding their interplay ensures robust data interpretation and decision-making. (data interpretation, statistical interplay, real-world applications)
Checklist for Applying 36 and 43.3
- Verify degrees of freedom (e.g., 36) in statistical tests.
- Analyze the context of values like 43.3 in machine learning models.
- Cross-check results to ensure consistency between calculations.
In summary, 36 and 43.3 are more than just numbers—they are critical components in data analysis. By mastering their significance, you can enhance your analytical accuracy and make informed decisions. Whether you’re conducting hypothesis tests or building machine learning models, these values play a pivotal role in shaping insights. (data analysis insights, analytical accuracy, informed decision-making)
What does 36 represent in statistical analysis?
+36 often represents degrees of freedom in statistical tests like t-tests and ANOVA, calculated as df = n - 1.
How is 43.3 used in machine learning?
+43.3 can represent critical thresholds, outliers, or regression coefficients in machine learning models.
Can 36 and 43.3 be used together in analysis?
+Yes, they can intersect in complex analyses, such as when degrees of freedom (36) influence the significance of a coefficient (43.3).