Arroyo Frog Population Growth: Key Factors & Trends

The Arroyo Frog, a species once on the brink of extinction, has seen a remarkable resurgence in recent years. This blog post delves into the key factors and trends driving the Arroyo Frog population growth, offering insights for conservationists, researchers, and nature enthusiasts alike. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for sustaining their recovery and ensuring their long-term survival. (Arroyo Frog conservation, population trends, wildlife preservation)
Habitat Restoration: A Cornerstone of Recovery
One of the most significant contributors to the Arroyo Frog population growth is habitat restoration. These frogs thrive in specific wetland environments, which have been severely impacted by urbanization and climate change. Efforts to restore natural water flows, replant native vegetation, and protect riparian zones have created ideal breeding grounds for Arroyo Frogs.
📌 Note: Successful habitat restoration requires collaboration between government agencies, conservation groups, and local communities.
Predator Control and Disease Management

Another critical factor in the Arroyo Frog population growth is the management of predators and diseases. Introduced species, such as non-native fish and birds, have historically preyed on Arroyo Frog eggs and tadpoles. Additionally, chytridiomycosis, a fungal disease, has posed a significant threat. Targeted predator control programs and disease monitoring have played a pivotal role in reducing these risks.
Climate Change and Its Impact

While habitat restoration and predator control have been successful, climate change remains a looming challenge for Arroyo Frog population growth. Altered rainfall patterns and increased temperatures can disrupt breeding cycles and reduce water availability. Adapting conservation strategies to mitigate these effects is essential for the species’ continued recovery.
Community Involvement and Education
Engaging local communities in conservation efforts has been instrumental in the Arroyo Frog population growth. Educational programs raise awareness about the importance of preserving wetland ecosystems and encourage citizens to participate in monitoring and restoration activities. This grassroots approach fosters a sense of stewardship and ensures long-term support for conservation initiatives.
| Factor | Impact on Population Growth |
|---|---|
| Habitat Restoration | Provides essential breeding grounds |
| Predator Control | Reduces threats to eggs and tadpoles |
| Climate Change Mitigation | Addresses long-term environmental challenges |
| Community Engagement | Ensures sustained conservation efforts |
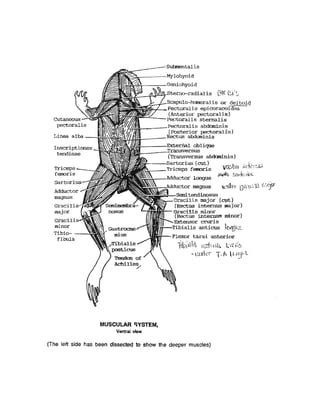
Monitoring and Research: Driving Informed Decisions
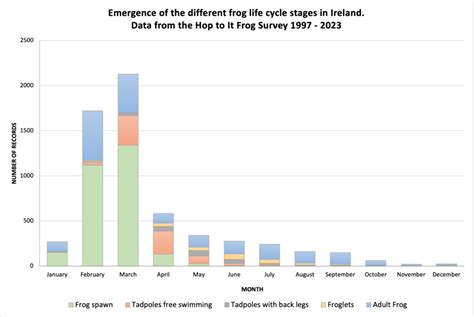
Continuous monitoring and research are vital for understanding the trends in Arroyo Frog population growth. Scientists use advanced techniques, such as genetic analysis and population modeling, to track their numbers and assess the effectiveness of conservation measures. This data-driven approach allows for adaptive management strategies that respond to changing conditions.
📌 Note: Regular monitoring helps identify emerging threats and ensures timely interventions.
The resurgence of the Arroyo Frog population is a testament to the power of targeted conservation efforts. By focusing on habitat restoration, predator control, climate change mitigation, community involvement, and scientific research, we can continue to support their growth and protect these unique amphibians for future generations. (Arroyo Frog recovery, conservation success, wetland preservation)
What are the main threats to Arroyo Frogs?
+
The main threats include habitat loss, predation by introduced species, disease (e.g., chytridiomycosis), and climate change.
How can individuals contribute to Arroyo Frog conservation?
+
Individuals can participate in local conservation programs, support wetland restoration projects, and spread awareness about the importance of preserving Arroyo Frog habitats.
What role does climate change play in Arroyo Frog population growth?
+
Climate change can disrupt breeding cycles, reduce water availability, and alter wetland ecosystems, posing long-term challenges to Arroyo Frog populations.