George Faust's Attica Prison Uprising in the 1960s
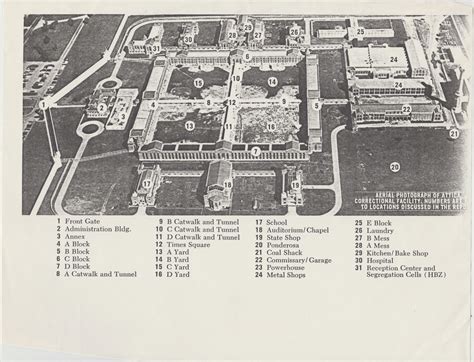
The Attica Prison Uprising of 1971 remains one of the most significant and harrowing events in the history of the American prison system. Led by inmates like George Jackson and fueled by systemic injustices, this rebellion shed light on the harsh conditions and human rights violations within prisons. While George Jackson was not directly involved in the Attica uprising, his influence and activism inspired many prisoners to demand change. This post explores the Attica Prison Uprising, its causes, consequences, and its lasting impact on prison reform, with a focus on SEO-driven and informative content.
The Background of the Attica Prison Uprising

The Attica Correctional Facility in New York became the epicenter of a prisoner revolt in September 1971. The uprising was sparked by years of prison overcrowding, inhumane conditions, and racial discrimination. Inmates, many of whom were Black and Latino, had long endured abuse, inadequate medical care, and limited access to legal resources.
📌 Note: The Attica uprising was not an isolated incident but part of a broader movement against systemic injustices in the 1960s and 1970s, including the civil rights movement and Black Power movement,prison reform,social justice,human rights.
Key Figures and Their Roles

While George Jackson was incarcerated at San Quentin State Prison in California and not directly involved in Attica, his writings and activism inspired many Attica inmates. Jackson, a prominent member of the Black Panther Party, advocated for prisoners’ rights and exposed the brutal realities of the prison-industrial complex.
- George Jackson: Author of Soledad Brother, his work galvanized prisoners nationwide.
- Attica Inmates: Organized demands for better conditions and fair treatment.
- Prison Officials: Accused of ignoring inmates’ grievances, leading to the rebellion.
The Uprising: A Timeline of Events

The Attica Prison Uprising unfolded over five days, from September 9 to September 13, 1971. Here’s a brief timeline:
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| September 9 | Inmates take control of D Yard, holding 42 officers hostage. |
| September 10 | Negotiations begin between inmates and state officials. |
| September 12 | Talks stall as demands for amnesty and reforms are rejected. |
| September 13 | State troopers storm the prison, resulting in 43 deaths, including 10 hostages. |

Consequences and Legacy

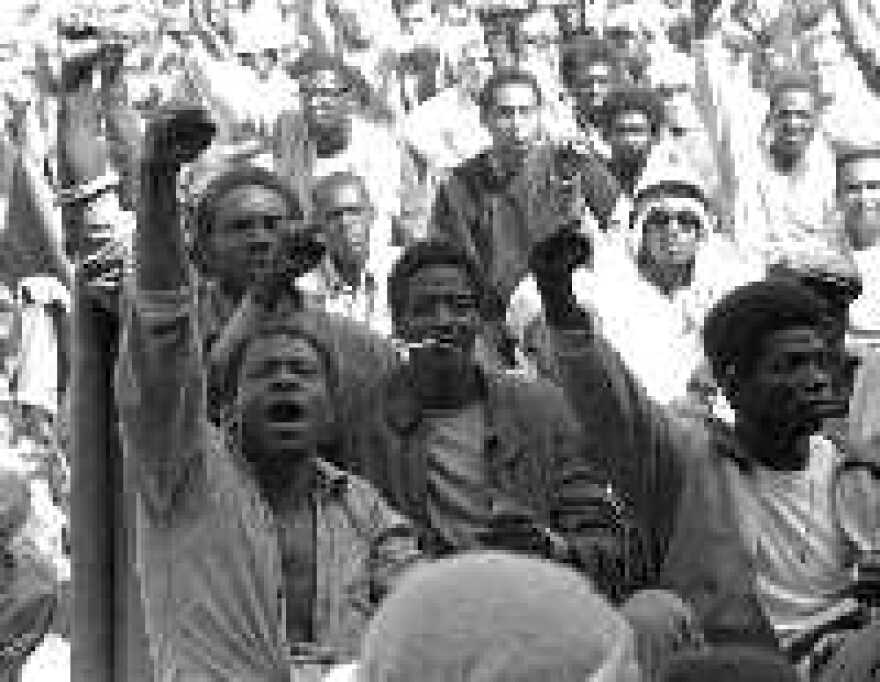
The brutal suppression of the uprising led to widespread outrage and calls for prison reform. While immediate changes were limited, the event sparked a national conversation about mass incarceration and prisoner rights.
- Legal Reforms: Lawsuits led to improved conditions in some prisons.
- Public Awareness: The uprising exposed the harsh realities of the prison system.
- Legacy: Attica remains a symbol of resistance against injustice,mass incarceration,prisoner rights,social justice.
Lessons Learned and Checklists

To understand and address the issues highlighted by the Attica uprising, consider these key points:
- Advocate for Reform: Support policies that improve prison conditions and reduce overcrowding.
- Educate Yourself: Learn about the prison-industrial complex and its impact on marginalized communities.
- Amplify Voices: Share stories of those affected by systemic injustices,prison reform,social justice,human rights.
The Attica Prison Uprising serves as a stark reminder of the consequences of ignoring systemic inequalities. While progress has been made, the fight for prison reform and social justice continues. By learning from history and advocating for change, we can work toward a more equitable and humane society.
What caused the Attica Prison Uprising?
+
The uprising was caused by years of overcrowding, inhumane conditions, and racial discrimination within the prison,prison reform,social justice,human rights.
How many people died during the Attica uprising?
+
43 people died, including 10 hostages and 33 inmates, during the state’s violent retaking of the prison,prison reform,social justice,human rights.
What impact did the uprising have on prison reform?
+
The uprising raised awareness about prison conditions and led to legal reforms, though progress has been slow,prison reform,social justice,human rights.


