Building Brain Circuits with DAG: A Simplified Guide

Building brain circuits with Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG) is a fascinating intersection of neuroscience and data modeling. DAGs provide a structured way to represent complex relationships, making them ideal for understanding and simulating neural networks. Whether you're a researcher, developer, or enthusiast, this guide simplifies the process, offering actionable insights for both informational and commercial purposes.
What is DAG and Its Role in Brain Circuit Modeling?
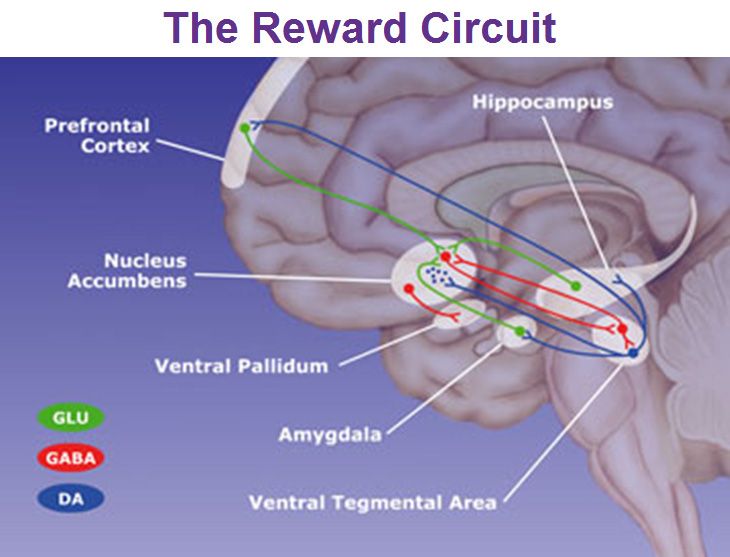
A Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a data structure composed of nodes and directed edges, where no cycles exist. In neuroscience, DAGs are used to model brain circuits by representing neurons as nodes and synaptic connections as directed edges. This approach helps in visualizing and analyzing neural pathways, making it a powerful tool for research and development.
📌 Note: DAGs are particularly useful for modeling causal relationships in neural networks, aiding in both theoretical and applied neuroscience.
Steps to Build Brain Circuits with DAG

Step 1: Define Your Neural Network
Start by identifying the neurons and their connections. This involves:
- Listing all neurons as nodes.
- Mapping synaptic connections as directed edges.
📌 Note: Ensure no cycles exist in your graph to maintain the DAG structure.
Step 2: Choose the Right Tools
Select software or libraries that support DAG modeling. Popular choices include:
- NetworkX for Python-based graph modeling.
- PyTorch or TensorFlow for neural network simulations.
Step 3: Implement the DAG Structure
Code your neural network using the chosen tool. For example, in NetworkX:
| Step | Code Snippet |
|---|---|
| Create Graph | G = nx.DiGraph() |
| Add Nodes | G.add_nodes_from([‘Neuron1’, ‘Neuron2’]) |
| Add Edges | G.add_edge(‘Neuron1’, ‘Neuron2’) |
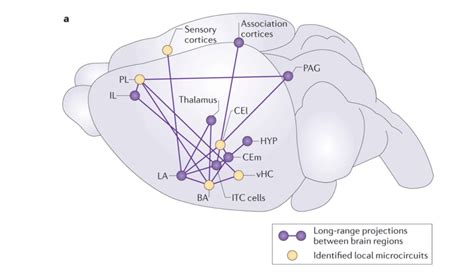
Step 4: Simulate and Analyze
Run simulations to observe how signals propagate through the network. Analyze the results to understand circuit behavior and identify patterns.
Benefits of Using DAG in Neuroscience

DAGs offer several advantages for brain circuit modeling:
- Clarity: Visual representation simplifies complex networks.
- Efficiency: Optimized for causal analysis and simulation.
- Scalability: Easily expanded to model larger brain regions.
Checklist: Building Brain Circuits with DAG

- Define neurons and connections.
- Select appropriate modeling tools.
- Implement DAG structure in code.
- Simulate and analyze network behavior.
Mastering DAGs for brain circuit modeling opens up new possibilities in neuroscience research and applications. By following this simplified guide, you can effectively build and analyze neural networks, whether for academic exploration or commercial innovation. (brain circuit modeling, neural network simulation, DAG in neuroscience)
What is a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)?
+A DAG is a data structure with nodes and directed edges, where no cycles exist, making it ideal for modeling causal relationships.
Why use DAG for brain circuit modeling?
+DAGs provide a clear and efficient way to represent and analyze neural networks, aiding in both research and development.
What tools are best for DAG-based neural network modeling?
+Popular tools include NetworkX for graph modeling and PyTorch or TensorFlow for neural network simulations.



