Chymotrypsin Digestion for Proteomic Analysis: A Quick Guide

<!DOCTYPE html>
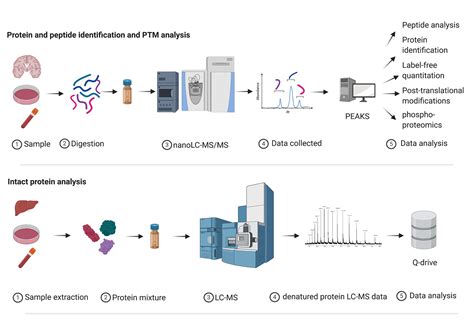
Chymotrypsin digestion is a critical step in proteomic analysis, enabling the breakdown of proteins into peptides for further study. This process is essential for identifying protein structures, functions, and post-translational modifications. Whether you're a researcher or a lab technician, understanding the nuances of chymotrypsin digestion can significantly enhance your proteomic workflows. Below, we’ll walk you through the key steps, best practices, and tips for successful digestion, ensuring accurate and reproducible results. (proteomic analysis, chymotrypsin digestion, protein breakdown)
Why Chymotrypsin Digestion is Essential for Proteomics
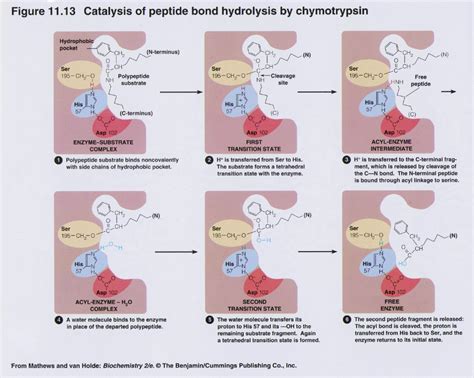
Chymotrypsin is a serine protease that cleaves peptide bonds at the carboxyl side of aromatic amino acids like phenylalanine, tryptophan, and tyrosine. This specificity makes it a valuable tool in proteomics, as it generates predictable peptide fragments suitable for mass spectrometry (MS) analysis. By using chymotrypsin, researchers can achieve higher sequence coverage and better identification of proteins compared to less specific enzymes. (serine protease, mass spectrometry, peptide fragments)
Step-by-Step Guide to Chymotrypsin Digestion
1. Prepare Your Protein Sample
Start by denaturing your protein sample in a buffer containing urea or guanidine hydrochloride. This step ensures the protein is fully unfolded, allowing chymotrypsin to access cleavage sites effectively. Reduce disulfide bonds using dithiothreitol (DTT) and alkylate with iodoacetamide to prevent re-formation. (protein denaturation, disulfide bond reduction, iodoacetamide alkylation)
2. Add Chymotrypsin to the Sample
Introduce chymotrypsin at a 1:50 to 1:100 enzyme-to-protein ratio. Ensure the pH is optimal, typically around 7.8–8.0, using a buffer like ammonium bicarbonate. Incubate the mixture at 37°C for 4–18 hours, depending on the sample complexity. (enzyme-to-protein ratio, incubation time, ammonium bicarbonate)
📌 Note: Avoid excessive incubation times, as they may lead to over-digestion and non-specific cleavage.
3. Stop the Digestion Process
After incubation, terminate the digestion by adding formic acid to lower the pH to ~3. This step inactivates chymotrypsin and prepares the sample for downstream analysis. (formic acid, digestion termination)
4. Desalt and Concentrate the Peptides
Use solid-phase extraction (SPE) or C18 spin columns to remove salts and concentrate the peptide mixture. This step ensures compatibility with MS analysis and improves data quality. (solid-phase extraction, C18 spin columns)
Best Practices for Optimal Results
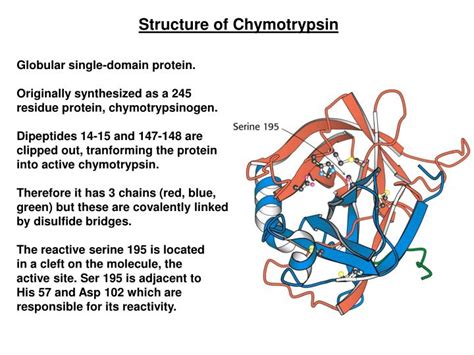
- Use high-quality chymotrypsin to minimize contamination and ensure consistent cleavage.
- Optimize enzyme concentration and incubation time based on your sample type.
- Store chymotrypsin at -20°C to maintain its activity and stability.
- Monitor digestion progress using SDS-PAGE or LC-MS for complex samples. (enzyme quality, incubation optimization, SDS-PAGE)
Troubleshooting Common Issues
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Incomplete digestion | Increase incubation time or enzyme concentration. |
| Non-specific cleavage | Reduce incubation time or use a fresher enzyme batch. |
| Low peptide yield | Check protein denaturation and buffer compatibility. |
Mastering chymotrypsin digestion is key to unlocking the full potential of proteomic analysis. By following these steps and best practices, you can achieve reliable and high-quality results in your research. Remember, consistency and attention to detail are crucial for success. (proteomic research, digestion troubleshooting, high-quality results)
What is the optimal pH for chymotrypsin digestion?
+The optimal pH for chymotrypsin digestion is between 7.8 and 8.0, typically achieved using ammonium bicarbonate buffer.
How long should chymotrypsin digestion be performed?
+Digestion times range from 4 to 18 hours, depending on sample complexity. Monitor progress to avoid over-digestion.
Can chymotrypsin digestion be used for all proteins?
+While chymotrypsin is effective for most proteins, some may require alternative enzymes for optimal cleavage.