col11a1 gene role in POAG and PACG glaucoma types

Glaucoma, a leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide, encompasses various types, including Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma (POAG) and Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma (PACG). Recent genetic studies have highlighted the role of the COL11A1 gene in these conditions, shedding light on potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Understanding the genetic underpinnings of glaucoma is crucial for early diagnosis, personalized treatment, and preventing vision loss.
What is the COL11A1 Gene?
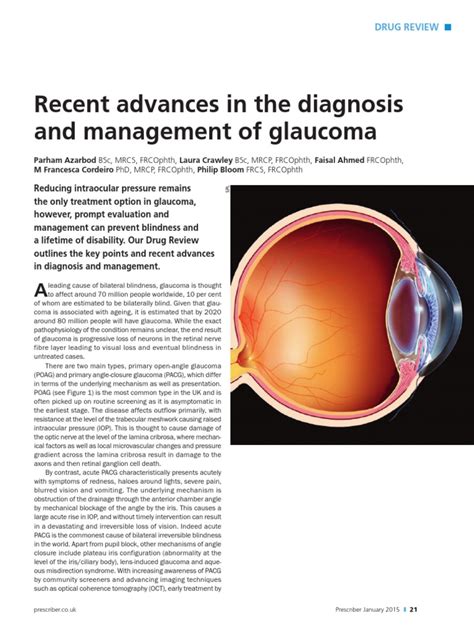
The COL11A1 gene encodes a component of type XI collagen, a protein essential for the structural integrity of connective tissues, including the eye. Mutations or variations in this gene have been linked to several ocular disorders, including glaucoma.
COL11A1 Gene and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma (POAG)
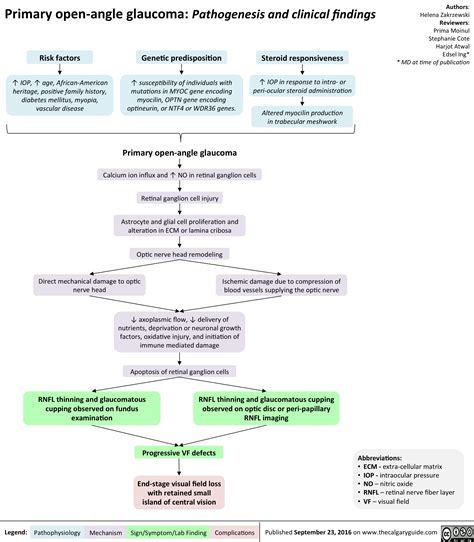
Role in Disease Pathogenesis
Research indicates that certain variants of the COL11A1 gene may contribute to the development of POAG by affecting the extracellular matrix of the optic nerve head and trabecular meshwork. This can lead to increased intraocular pressure (IOP), a primary risk factor for glaucoma.
Clinical Implications
Identifying COL11A1 gene variants in patients with POAG could help in early detection and personalized management strategies. Genetic testing may become a valuable tool for ophthalmologists to assess glaucoma risk and tailor treatments.
📌 Note: Genetic testing for COL11A1 variants is not yet standard in clinical practice but shows promise for future glaucoma management.
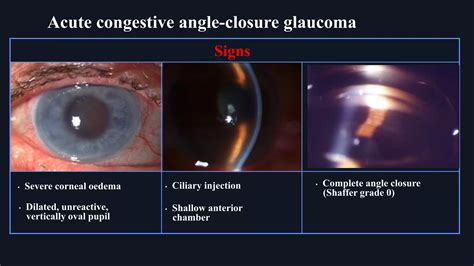
COL11A1 Gene and Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma (PACG)
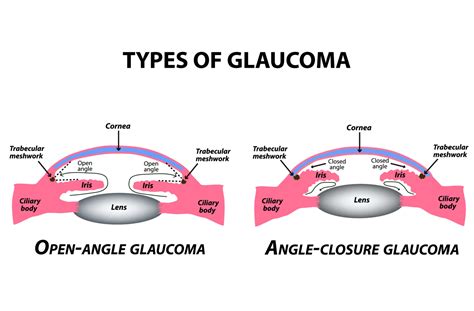
Genetic Association
While PACG is primarily associated with anatomical factors like a shallow anterior chamber, recent studies suggest that COL11A1 gene variations may influence the structural changes leading to angle closure. These variations could affect the scleral and corneal tissues, contributing to the disease.
Potential Therapeutic Insights
Understanding the role of COL11A1 in PACG may open avenues for novel therapies targeting collagen-related pathways. This could complement existing treatments like laser iridotomy and medications to lower IOP.
| Glaucoma Type | COL11A1 Gene Role | Clinical Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| POAG | Affects optic nerve head and trabecular meshwork | Early detection and personalized treatment |
| PACG | Influences scleral and corneal structure | Potential for novel therapies |
Checklist for Glaucoma Management
- Regular Eye Exams: Early detection is key to managing glaucoma effectively.
- Genetic Testing: Consider genetic screening for high-risk individuals or those with a family history of glaucoma.
- IOP Monitoring: Regularly measure intraocular pressure to assess disease progression.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintain a healthy lifestyle to reduce glaucoma risk factors.
What is the COL11A1 gene?
+The COL11A1 gene encodes a component of type XI collagen, essential for connective tissue integrity, including the eye.
How does COL11A1 contribute to POAG?
+COL11A1 variants may affect the optic nerve head and trabecular meshwork, leading to increased intraocular pressure, a key factor in POAG.
Can COL11A1 testing predict glaucoma risk?
+While not yet standard, COL11A1 genetic testing shows potential for assessing glaucoma risk, especially in high-risk populations.
The COL11A1 gene plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of both POAG and PACG, offering insights into genetic factors contributing to glaucoma. Advances in genetic research may lead to improved diagnostic tools and targeted therapies, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes. Regular eye exams and awareness of genetic risk factors remain essential for early intervention and prevention of vision loss. (glaucoma genetic testing, glaucoma prevention, COL11A1 gene research)