Understanding Cytoplasm Reactions: A Simplified Model Explained
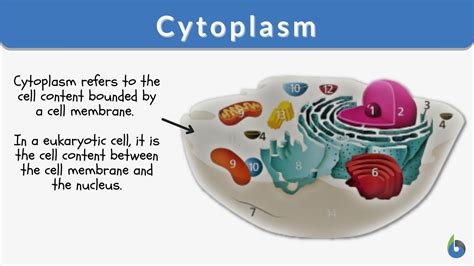
Cytoplasm reactions are fundamental processes that occur within the cells of living organisms, playing a crucial role in maintaining cellular functions. Understanding these reactions can provide valuable insights into cell biology, metabolism, and even disease mechanisms. In this post, we’ll explore a simplified model of cytoplasm reactions, breaking down complex concepts into digestible information for both informational and commercial audiences. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or simply curious about cellular processes, this guide will help you grasp the essentials of cytoplasm reactions, cytoplasm function, and their significance in biology.
What Are Cytoplasm Reactions?
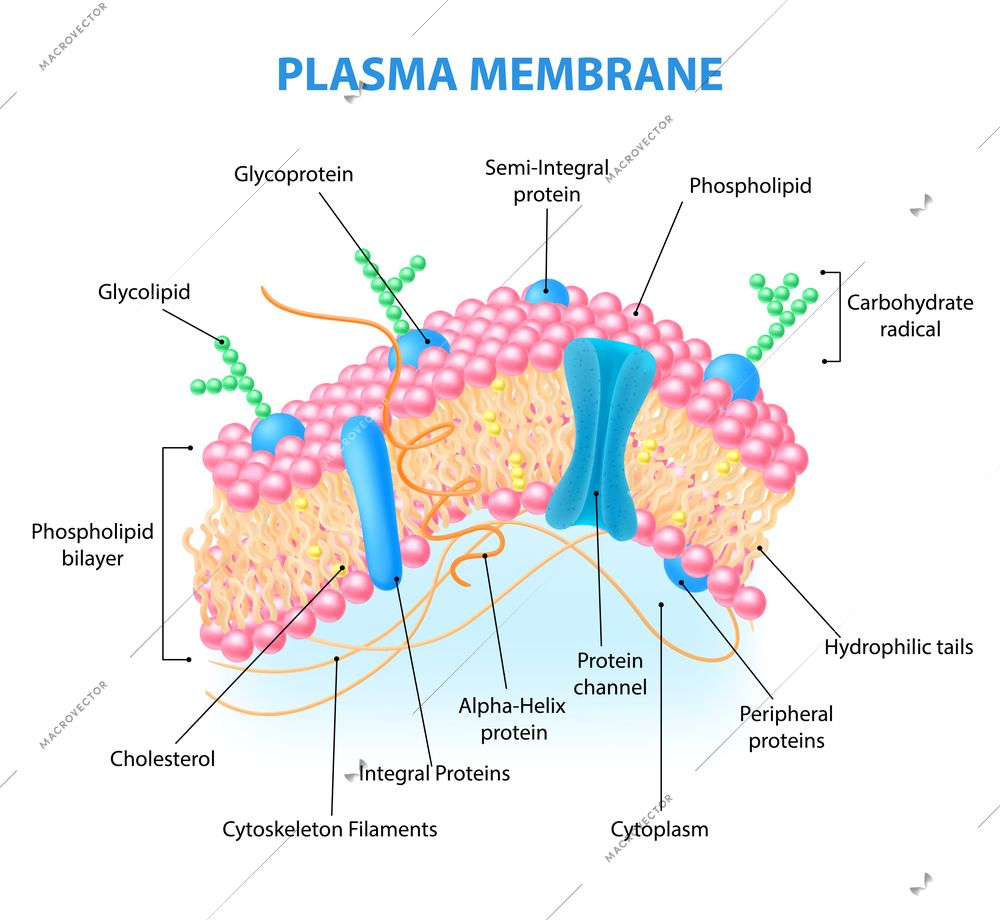
Cytoplasm reactions refer to the chemical processes that take place within the cytoplasm, the gel-like substance inside cells. These reactions are essential for energy production, synthesis of biomolecules, and overall cellular homeostasis. Key processes include metabolism, enzymatic reactions, and signal transduction. Understanding these reactions is vital for fields like biochemistry, molecular biology, and pharmaceutical research.
📌 Note: The cytoplasm acts as a medium for these reactions, providing the necessary environment for enzymes and molecules to interact efficiently.
The Simplified Model of Cytoplasm Reactions

To make cytoplasm reactions easier to understand, we’ll break them down into three core components:
- Substrates: The molecules on which enzymes act, such as glucose in glycolysis.
- Enzymes: Biological catalysts that speed up reactions, like ATP synthase in energy production.
- Products: The end results of reactions, such as ATP or waste molecules.
This model highlights the dynamic interplay between these elements, which is essential for cytoplasm function and cellular survival.
Key Cytoplasm Reactions Explained
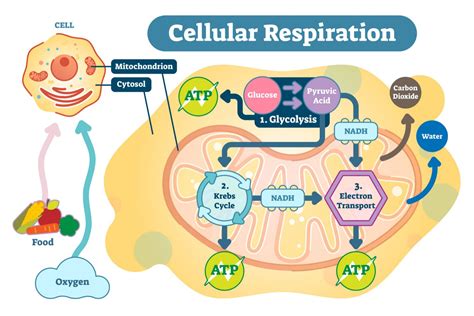
1. Glycolysis
Glycolysis is a central metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose into pyruvate, producing ATP and NADH. This reaction occurs in the cytoplasm and is crucial for energy generation, especially in anaerobic conditions.
2. Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis involves the translation of mRNA into proteins, a process facilitated by ribosomes in the cytoplasm. This reaction is vital for cell growth, repair, and function.
3. Signal Transduction Pathways
These pathways allow cells to respond to external signals, such as hormones or growth factors. Cytoplasmic enzymes play a key role in transmitting these signals to the nucleus or other cellular components.
| Reaction | Location | Key Enzymes | Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycolysis | Cytoplasm | Hexokinase, Phosphofructokinase | ATP, Pyruvate |
| Protein Synthesis | Cytoplasm (Ribosomes) | Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase | Proteins |
| Signal Transduction | Cytoplasm | Protein Kinases | Activated Proteins |
Practical Applications of Cytoplasm Reactions
Understanding cytoplasm reactions has significant implications in various fields:
- Medicine: Studying these reactions helps in developing treatments for metabolic disorders and cancer.
- Biotechnology: Enzymes from cytoplasmic reactions are used in industrial processes like fermentation.
- Education: Simplified models aid in teaching complex cellular processes to students.
💡 Note: Commercial applications often focus on optimizing enzymes for efficiency in biotechnological processes.
In summary, cytoplasm reactions are essential for cellular function, involving substrates, enzymes, and products in a dynamic interplay. From glycolysis to protein synthesis, these reactions underpin life processes and have wide-ranging applications in science and industry. By understanding this simplified model, you can appreciate the complexity and beauty of cellular biology, cytoplasm function, and its practical implications.
Checklist for Understanding Cytoplasm Reactions

- Learn the roles of substrates, enzymes, and products.
- Study key reactions like glycolysis and protein synthesis.
- Explore practical applications in medicine and biotechnology.
- Use simplified models to teach or learn complex concepts.
What is the main function of the cytoplasm?
+The cytoplasm serves as the site for metabolic reactions, supports cell structure, and facilitates movement of molecules within the cell.
How do enzymes contribute to cytoplasm reactions?
+Enzymes act as catalysts, speeding up reactions in the cytoplasm without being consumed in the process.
Why are cytoplasm reactions important in biotechnology?
+Cytoplasmic enzymes are used in biotechnological processes like fermentation and drug production, making them valuable in industry.
cytoplasm function, cellular reactions, metabolic pathways, enzymatic processes, cell biology, biotechnology applications, glycolysis, protein synthesis.