Understanding Day Time Periastron: Key Facts & Insights

Day Time Periastron is a critical concept in astronomy, particularly in the study of binary star systems and exoplanets. It refers to the point in an orbit when two celestial bodies are closest to each other, occurring during the day. Understanding this phenomenon is essential for astronomers, astrophysicists, and space enthusiasts alike. This post delves into the key facts and insights about Day Time Periastron, providing valuable information for both informational and commercial audiences, celestial mechanics, orbital dynamics, binary star systems.
What is Day Time Periastron?
Day Time Periastron is the moment in a binary system’s orbit when the two objects are at their minimum separation, and this event happens during daylight hours. This phenomenon is crucial for studying gravitational interactions, tidal forces, and energy exchanges between the orbiting bodies, gravitational interactions, tidal forces, energy exchanges.
Key Facts About Day Time Periastron
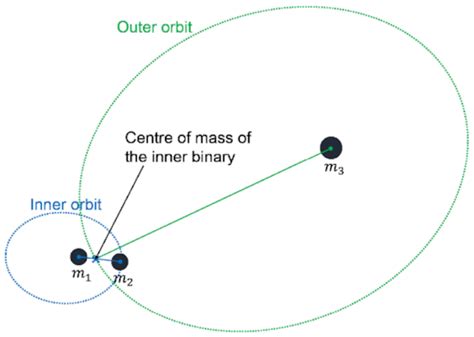
Orbital Mechanics
The occurrence of Day Time Periastron depends on the orbital parameters of the binary system, including eccentricity, semi-major axis, and inclination. These factors determine the timing and frequency of periastron passages, orbital parameters, eccentricity, semi-major axis.
Observational Challenges
Observing Day Time Periastron can be challenging due to the bright daylight conditions, which may obscure the celestial bodies. Advanced telescopes and filters are often required to capture accurate data, observational techniques, advanced telescopes, data analysis.
Insights and Applications

Exoplanet Discoveries
Studying Day Time Periastron has led to significant discoveries in exoplanet research. The gravitational effects during periastron can cause detectable changes in the host star’s light, enabling the identification of new planets, exoplanet research, gravitational effects, planet detection.
Commercial Opportunities
For commercial entities, understanding Day Time Periastron opens avenues in space tourism and satellite technology. Predicting periastron events can optimize satellite orbits and enhance space travel experiences, space tourism, satellite technology, orbit optimization.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Eccentricity | Measures the elongation of the orbit |
| Semi-Major Axis | Half the longest diameter of the elliptical orbit |
📌 Note: Accurate prediction of Day Time Periastron requires precise orbital data and advanced computational models.
Checklist for Observing Day Time Periastron

- Verify orbital parameters of the binary system
- Use specialized telescopes with daylight filters
- Analyze data for gravitational anomalies
- Correlate findings with exoplanet databases
Day Time Periastron is a fascinating aspect of celestial mechanics with wide-ranging implications. From advancing exoplanet research to creating commercial opportunities, its study is invaluable. By understanding the orbital mechanics and overcoming observational challenges, scientists and businesses can harness the potential of this phenomenon, celestial mechanics, orbital mechanics, observational challenges.
What causes Day Time Periastron?
+Day Time Periastron is caused by the elliptical nature of orbits in binary systems, where the closest approach occurs during daylight hours.
How is Day Time Periastron observed?
+Observation requires specialized telescopes with daylight filters and advanced data analysis techniques to detect subtle changes during periastron.
What are the commercial applications of Day Time Periastron?
+Commercial applications include optimizing satellite orbits, enhancing space tourism experiences, and improving space technology.