Eigenvalues of Stokes' Operator Explained Simply

Understanding the eigenvalues of Stokes’ operator is crucial for anyone delving into fluid dynamics, partial differential equations, or mathematical physics. These eigenvalues play a pivotal role in analyzing the behavior of incompressible flows, making them a fundamental concept in both theoretical and applied mathematics. In this post, we’ll break down the topic into digestible sections, ensuring clarity for both informational and commercial audiences.
What Are Eigenvalues of Stokes’ Operator?
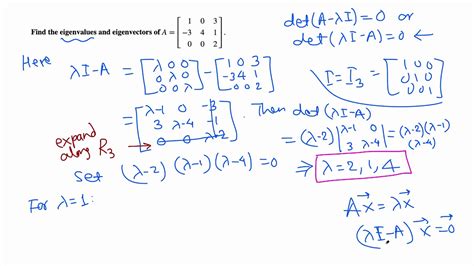
The Stokes’ operator arises from the study of the Stokes equations, which describe the motion of incompressible fluids at low Reynolds numbers. Eigenvalues of this operator represent the critical frequencies or modes at which the fluid system oscillates or decays. They provide insights into the stability and dynamics of fluid flows, making them essential in fields like engineering, meteorology, and oceanography.
💡 Note: Eigenvalues are scalar values that, when multiplied by a corresponding eigenfunction, yield the same function after the operator is applied.
Why Are Eigenvalues of Stokes’ Operator Important?

Eigenvalues help mathematicians and engineers:
- Analyze fluid stability: Determine whether a flow is stable or prone to turbulence.
- Solve partial differential equations: Simplify complex equations governing fluid motion.
- Optimize engineering designs: Improve the efficiency of systems involving fluid dynamics, such as pumps, pipelines, or aircraft wings.
For commercial audiences, understanding these eigenvalues can lead to better product designs, cost savings, and enhanced performance in fluid-related applications.
How to Compute Eigenvalues of Stokes’ Operator
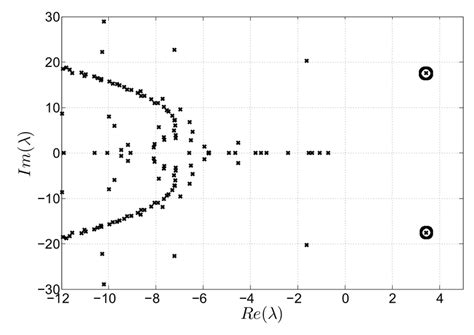
Computing these eigenvalues involves solving a spectral problem derived from the Stokes equations. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
1. Formulate the Stokes problem: Start with the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations and linearize them.
2. Apply boundary conditions: Define the domain and constraints of the fluid system.
3. Solve the eigenvalue problem: Use numerical methods like finite element analysis or spectral methods to find the eigenvalues.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Formulate the Stokes problem |
| 2 | Apply boundary conditions |
| 3 | Solve the eigenvalue problem |
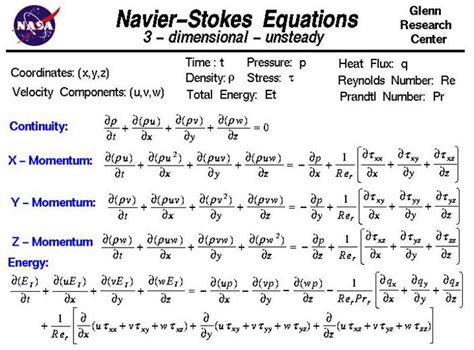
📌 Note: Numerical methods are often necessary due to the complexity of analytical solutions.
Applications of Eigenvalues in Fluid Dynamics

Eigenvalues of Stokes’ operator have wide-ranging applications:
- Turbulence modeling: Predicting and controlling turbulent flows.
- Heat transfer: Analyzing fluid behavior in thermal systems.
- Biomedical engineering: Studying blood flow in arteries and veins.
For commercial audiences, these applications translate into innovations in HVAC systems, automotive design, and medical devices.
Key Takeaways
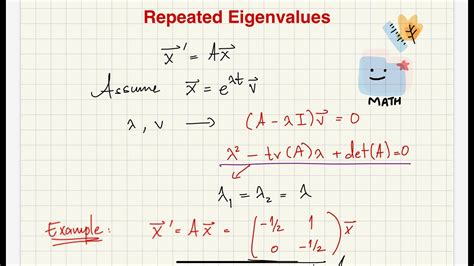
- Eigenvalues of Stokes’ operator are critical for understanding fluid dynamics.
- They simplify complex equations and provide insights into flow stability.
- Computational methods are essential for their calculation.
What are eigenvalues in fluid dynamics?
+Eigenvalues represent critical frequencies or modes in fluid systems, helping analyze stability and dynamics.
How are eigenvalues of Stokes' operator computed?
+They are computed by solving a spectral problem derived from the Stokes equations, often using numerical methods.
What are the practical applications of these eigenvalues?
+Applications include turbulence modeling, heat transfer analysis, and biomedical engineering.
In summary, the eigenvalues of Stokes’ operator are a cornerstone of fluid dynamics, offering both theoretical insights and practical applications. Whether you’re a researcher, engineer, or industry professional, mastering this concept can unlock new possibilities in your work.
Stokes’ equations,fluid dynamics,eigenvalue problems,numerical methods,turbulence modeling,heat transfer analysis,biomedical engineering.



