Understanding the Epidermis: Melanin's Role Simplified
The skin, our body’s largest organ, plays a vital role in protecting us from external elements. At the forefront of this defense is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Central to its function is melanin, a pigment that not only gives our skin its color but also shields it from harmful UV rays. Understanding melanin’s role in the epidermis is key to appreciating how our skin works and how to care for it effectively. (skin health, melanin function, UV protection)
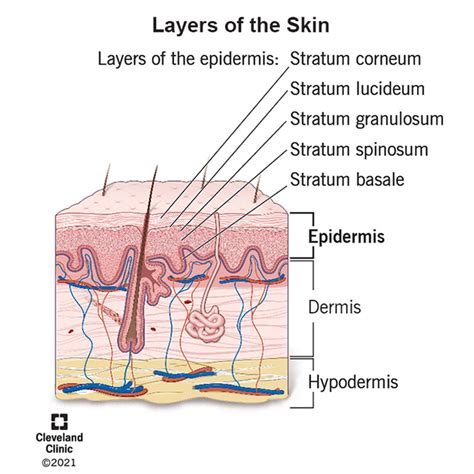
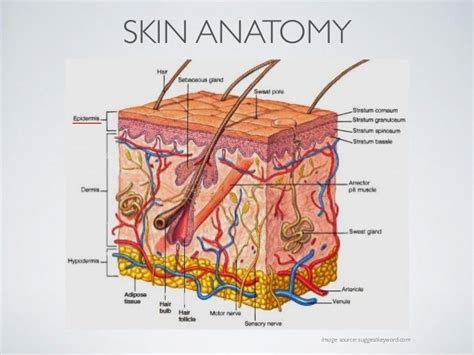
What is the Epidermis?
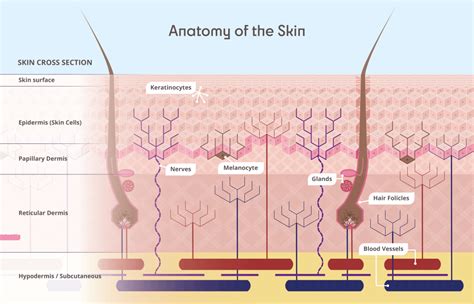
The epidermis is the top layer of the skin, acting as a barrier against bacteria, viruses, and other environmental threats. It consists of multiple layers, each with specific functions. The outermost layer, the stratum corneum, is composed of dead skin cells that continually shed and renew. This process is essential for maintaining healthy skin. (epidermis structure, skin barrier, skin renewal)
Melanin: The Skin’s Natural Protector
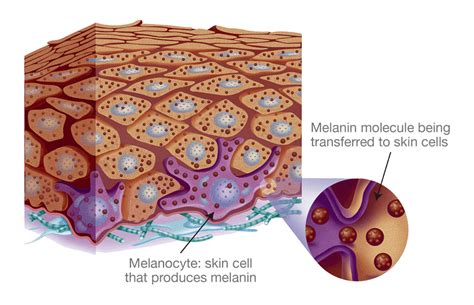
Melanin is a pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes, located in the epidermis. Its primary role is to protect the skin from the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Melanin absorbs and scatters UV rays, preventing them from damaging the skin’s DNA. This is why people with higher melanin levels tend to have darker skin and are less prone to sunburn. (melanin production, UV protection, skin pigmentation)
How Melanin Works
When the skin is exposed to sunlight, melanocytes produce more melanin as a defense mechanism. This process, known as melanogenesis, results in tanning. However, excessive sun exposure can overwhelm this protective system, leading to sun damage, premature aging, and even skin cancer. (melanogenesis, tanning, sun damage)
☀️ Note: Wearing sunscreen with at least SPF 30 is crucial to support melanin’s protective function and prevent skin damage.
Melanin and Skin Tone
The amount and type of melanin produced determine an individual’s skin tone. There are two primary types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. Eumelanin provides a brown-black color and offers stronger UV protection, while pheomelanin produces a red-yellow hue and provides less protection. (skin tone, eumelanin, pheomelanin)
Melanin Imbalance and Skin Conditions
An overproduction or underproduction of melanin can lead to various skin conditions:
- Hyperpigmentation: Dark patches caused by excess melanin.
- Hypopigmentation: Light patches due to reduced melanin.
- Albinism: A genetic condition where little to no melanin is produced.
Understanding these conditions can help in choosing the right skincare products and treatments. (hyperpigmentation, hypopigmentation, albinism)
| Condition | Cause | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Hyperpigmentation | Excess melanin production | Topical creams, laser therapy |
| Hypopigmentation | Reduced melanin production | Cosmetic cover-ups, UV protection |
| Albinism | Genetic lack of melanin | Sunscreen, protective clothing |

How to Support Melanin Function
To maintain healthy melanin production and protect your skin:
- Use Sunscreen Daily: Shield your skin from UV damage.
- Stay Hydrated: Healthy skin starts from within.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Opt for gentle skincare products.
- Eat Melanin-Boosting Foods: Include antioxidants like berries, carrots, and leafy greens in your diet.
(sunscreen use, skincare routine, melanin-boosting diet)
Final Thoughts
Melanin is more than just a pigment; it’s a crucial component of the epidermis that safeguards our skin from harm. By understanding its role and taking proactive steps to support it, we can maintain healthy, radiant skin. Remember, protecting your skin today ensures its health tomorrow. (skin protection, healthy skin, melanin care)
What is the main function of melanin in the epidermis?
+
Melanin primarily protects the skin from harmful UV radiation by absorbing and scattering UV rays.
Can melanin production be increased naturally?
+
While melanin production is largely genetic, consuming antioxidant-rich foods and avoiding excessive sun exposure can support healthy melanin function.
What causes hyperpigmentation?
+
Hyperpigmentation is caused by an overproduction of melanin, often triggered by sun exposure, hormonal changes, or skin injuries.



