Unveiling the Goals of Tanzimat Reforms: A Concise Overview

The Tanzimat Reforms, initiated in the Ottoman Empire during the 19th century, mark a pivotal era of modernization and restructuring. Aimed at revitalizing the empire’s administrative, legal, and economic systems, these reforms sought to address internal challenges and external pressures. This concise overview delves into the primary goals of the Tanzimat Reforms, shedding light on their significance in Ottoman history and their lasting impact on the region, Ottoman history, modernization efforts, administrative reforms.
Understanding the Tanzimat Reforms

The Tanzimat Reforms, spanning from 1839 to 1876, were a series of reforms designed to modernize the Ottoman Empire. Facing territorial losses and internal strife, the Ottoman leadership sought to strengthen the empire by adopting Western-inspired policies. The reforms were formalized through the Hatt-ı Şerif of Gülhane (Noble Edict of the Rose Chamber) in 1839, which laid the groundwork for administrative, legal, and social changes, Ottoman Empire, 19th-century reforms, Hatt-ı Şerif of Gülhane.
Key Goals of the Tanzimat Reforms

The reforms were driven by several core objectives:
1. Centralizing Administrative Power
One of the primary goals was to centralize authority and streamline governance. The reforms aimed to reduce the influence of local leaders and create a more efficient bureaucratic system. This included standardizing tax collection, improving public services, and establishing a modern civil service, administrative reforms, centralized governance, bureaucratic modernization.
2. Modernizing Legal Systems
The Tanzimat Reforms sought to replace traditional Islamic law with a secular legal framework. The Mecelle, a civil code introduced in 1869, blended Islamic principles with modern legal concepts. Additionally, non-Muslim subjects were granted equal rights under the law, marking a significant shift toward equality, legal reforms, Mecelle, secularization, equality for minorities.
3. Strengthening the Economy
Economic revitalization was a key focus. The reforms encouraged foreign investment, improved infrastructure, and promoted industrialization. However, these efforts often led to increased foreign influence and debt, creating long-term challenges for the empire, economic reforms, foreign investment, industrialization, Ottoman economy.
📌 Note: While the Tanzimat Reforms aimed to modernize the Ottoman Empire, they also exposed it to greater foreign intervention and economic dependency.
Impact and Legacy of the Tanzimat Reforms

Though the reforms achieved partial success in modernizing the empire, they faced significant obstacles. Resistance from conservative factions, financial instability, and external pressures limited their effectiveness. Nonetheless, the Tanzimat Reforms laid the foundation for future modernization efforts in the region, legacy of Tanzimat, modernization challenges, Ottoman decline.
Final Reflections
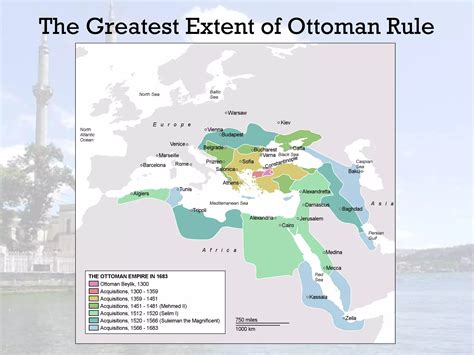
The Tanzimat Reforms represent a critical chapter in Ottoman history, reflecting the empire’s struggle to adapt to a changing world. By centralizing administration, modernizing laws, and revitalizing the economy, these reforms sought to secure the Ottoman Empire’s future. While their success was mixed, their legacy continues to influence discussions on governance, law, and modernization in the Middle East, Ottoman legacy, Middle Eastern history, governance reforms.
What were the main goals of the Tanzimat Reforms?
+
The main goals included centralizing administrative power, modernizing legal systems, and strengthening the economy to revitalize the Ottoman Empire.
What was the Hatt-ı Şerif of Gülhane?
+
The Hatt-ı Şerif of Gülhane, issued in 1839, was the noble edict that formally initiated the Tanzimat Reforms, outlining the empire’s modernization agenda.
How did the Tanzimat Reforms impact non-Muslim subjects?
+
The reforms granted non-Muslim subjects equal rights under the law, marking a significant step toward religious and legal equality in the Ottoman Empire.



