Phosphorus Deficiency in Plants: Fungus or Nutrient Issue?

Phosphorus deficiency in plants can manifest as stunted growth, purple leaves, or poor root development, leaving gardeners puzzled. Is it a fungus or a nutrient issue? Understanding the root cause is crucial for effective treatment. While fungi can sometimes mimic nutrient deficiencies, phosphorus deficiency is primarily a soil or uptake problem. This post will guide you through identifying symptoms, causes, and solutions, ensuring your plants thrive. (phosphorus deficiency symptoms, plant nutrient issues)
Identifying Phosphorus Deficiency in Plants

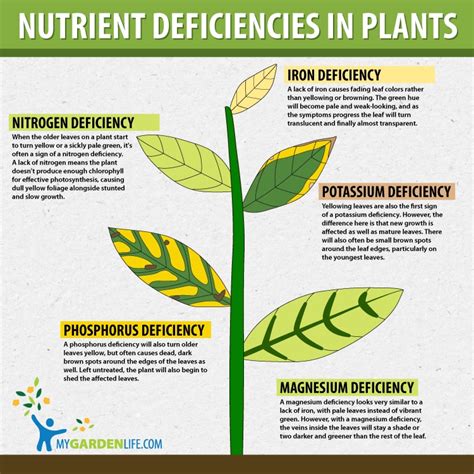
Phosphorus is vital for energy transfer, root growth, and flowering. When plants lack phosphorus, they show distinct signs:
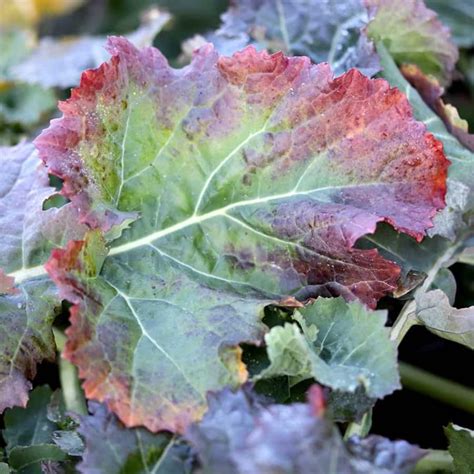
- Purple or reddish leaves, especially in older foliage.
- Stunted growth and weak root systems.
- Delayed maturity and poor fruit or flower development.
These symptoms can resemble fungal infections, but they are often linked to soil conditions or nutrient imbalances. (plant health, nutrient deficiency)
Fungus vs. Nutrient Issue: What’s the Difference?
Fungal infections like Phytophthora or Fusarium can cause root rot, leading to nutrient uptake problems. However, phosphorus deficiency is typically caused by:
- Soil pH imbalances (phosphorus becomes unavailable in highly acidic or alkaline soils).
- Cold soil temperatures, which slow phosphorus uptake.
- Insufficient phosphorus in the soil due to poor fertilization.
To differentiate, inspect roots for fungal signs (discoloration, rot) and test soil phosphorus levels. (soil testing, fungal diseases)
Solutions for Phosphorus Deficiency

Addressing phosphorus deficiency involves both short-term fixes and long-term strategies:
- Apply phosphorus-rich fertilizers like bone meal or rock phosphate.
- Adjust soil pH to the optimal range (6.0–7.0) for phosphorus availability.
- Improve soil structure with organic matter to enhance nutrient uptake.
For commercial growers, consider foliar sprays or slow-release fertilizers for quick results. (organic gardening, soil amendments)
Preventing Phosphorus Deficiency

Prevention is key to healthy plants:
- Test soil annually to monitor phosphorus levels.
- Rotate crops to avoid nutrient depletion.
- Use compost to maintain soil fertility.
💡 Note: Over-fertilization can lead to phosphorus runoff, harming the environment. Always follow recommended application rates.
Checklist for Managing Phosphorus Deficiency
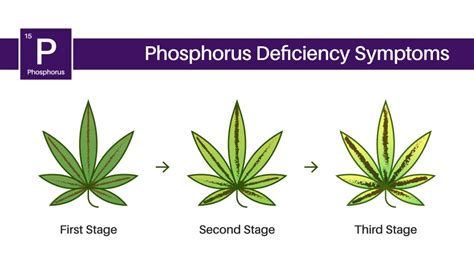
- Inspect leaves for purple discoloration.
- Test soil pH and phosphorus levels.
- Apply appropriate fertilizers or amendments.
- Monitor soil temperature and moisture.
- Keep records for future reference.
Phosphorus deficiency in plants is often a nutrient issue rather than a fungal problem. By understanding symptoms, causes, and solutions, you can effectively address the issue and promote healthy plant growth. Regular soil testing and proper fertilization are your best tools for prevention. (plant care, gardening tips)
Can phosphorus deficiency be fixed quickly?
+
Yes, foliar sprays or water-soluble fertilizers can provide quick relief, but long-term solutions like soil amendments are recommended.
How do I test my soil for phosphorus?
+
Use a soil testing kit or send a sample to a lab for accurate phosphorus and pH readings.
Can over-fertilization cause phosphorus deficiency?
+
Yes, excessive nutrients can disrupt soil balance, making phosphorus unavailable to plants.



