Metal Indentation: Load, Depth, Displacement, Burst Explained

Opening Paragraph:
Metal indentation testing is a critical process used to evaluate the hardness and durability of materials. By applying a controlled load, measuring depth, displacement, and observing burst characteristics, engineers and manufacturers can ensure material quality and performance. Whether you’re in the automotive, aerospace, or manufacturing industry, understanding these parameters is essential for optimizing material selection and product reliability. (metal hardness testing, material durability, indentation analysis)
What is Metal Indentation Testing?

Metal indentation testing involves applying a specific force (load) to a material’s surface using an indenter. The resulting depth and displacement provide insights into the material’s hardness and resistance to deformation. Burst, on the other hand, refers to the material’s failure point under extreme pressure. This test is widely used in quality control and research to assess material behavior under stress. (metal indentation testing, material hardness, deformation analysis)
Key Parameters in Metal Indentation

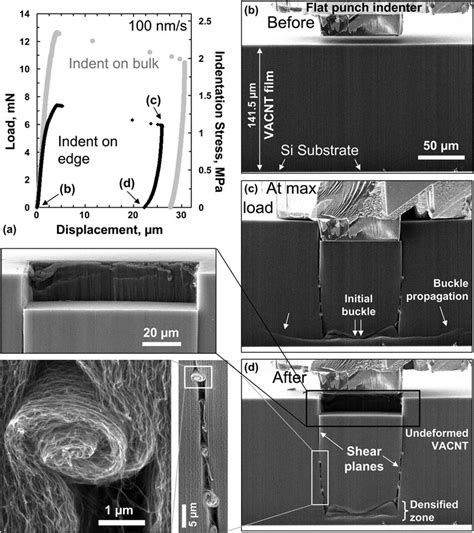
1. Load: The Applied Force
The load is the force applied during the indentation process. It is typically measured in Newtons (N) or kilograms-force (kgf). The load directly influences the depth and displacement, with higher loads resulting in greater indentation. Selecting the appropriate load is crucial to avoid material damage while obtaining accurate results. (indentation load, force measurement, material testing)
2. Depth: Measuring Material Penetration
Depth refers to how far the indenter penetrates the material’s surface. It is measured in micrometers (μm) and is a key indicator of material hardness. Deeper indentations suggest softer materials, while shallow ones indicate harder surfaces. Precision in depth measurement is vital for reliable testing. (indentation depth, material penetration, hardness measurement)
3. Displacement: Understanding Material Movement
Displacement measures the lateral movement of the material during indentation. It provides insights into the material’s elasticity and plasticity. High displacement values indicate greater material deformation, while low values suggest higher rigidity. Analyzing displacement helps in predicting material performance under different conditions. (material displacement, elasticity testing, plasticity analysis)
4. Burst: The Breaking Point
Burst occurs when the material fails under extreme pressure, causing it to crack or fracture. This parameter is critical for understanding the material’s maximum load-bearing capacity. Observing burst characteristics helps in identifying material weaknesses and improving design resilience. (material burst, failure analysis, load-bearing capacity)
| Parameter | Unit of Measurement | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Load | N or kgf | Applied force |
| Depth | μm | Material hardness |
| Displacement | μm | Material deformation |
| Burst | N or kgf | Material failure point |

📌 Note: Accurate measurement of these parameters requires calibrated equipment and standardized testing procedures.
Applications of Metal Indentation Testing

Metal indentation testing is used across industries for:
- Quality Control: Ensuring materials meet specified standards.
- Research & Development: Studying material behavior under stress.
- Product Design: Optimizing material selection for durability.
- Failure Analysis: Identifying causes of material failure. (quality control, material research, product design)
Checklist for Effective Metal Indentation Testing
- Select the Right Load: Ensure it aligns with material properties.
- Calibrate Equipment: Use precise tools for accurate measurements.
- Analyze Depth & Displacement: Correlate results with material hardness and deformation.
- Monitor Burst: Identify failure points for safety and design improvements.
- Document Results: Maintain records for future reference and analysis. (testing checklist, calibration, result analysis)
Final Thoughts:
Understanding metal indentation parameters—load, depth, displacement, and burst—is crucial for assessing material performance and ensuring product reliability. By mastering these concepts, industries can enhance quality control, innovate in material research, and optimize product designs. Whether you’re a manufacturer or researcher, this knowledge is indispensable for achieving excellence in material testing. (material performance, product reliability, testing excellence)
What is the purpose of metal indentation testing?
+
Metal indentation testing evaluates material hardness, deformation, and failure points under controlled loads, ensuring quality and performance.
How is indentation depth measured?
+
Depth is measured in micrometers (μm) using precision tools to determine how far the indenter penetrates the material’s surface.
Why is burst analysis important?
+
Burst analysis identifies the material’s failure point under extreme pressure, helping improve safety and design resilience.