Unraveling Multiple Order Poles in Complex Analysis: A Simplified Guide

Understanding multiple order poles in complex analysis can be a daunting task, but with the right approach, it becomes manageable. This guide simplifies the concept, breaking it down into digestible steps for both students and professionals. Whether you’re tackling complex analysis for academic purposes or applying it in engineering and physics, this post will help you grasp the essentials. From defining poles to analyzing their behavior, we’ll cover everything you need to know. Let’s dive in and unravel the mysteries of multiple order poles together. (complex analysis, multiple order poles, residue calculus)
What Are Multiple Order Poles in Complex Analysis?
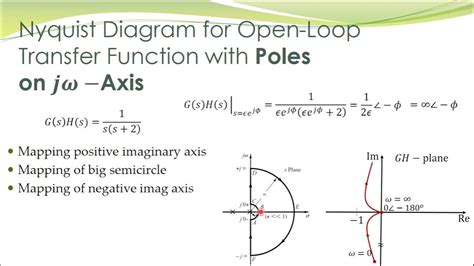
In complex analysis, a pole is a singularity of a function where the function approaches infinity. A multiple order pole occurs when this singularity has a multiplicity greater than one. Essentially, it’s a point where the function behaves like , with . Understanding these poles is crucial for residue calculus, which is widely used in integration and solving real-world problems. (complex analysis, poles, residue calculus)
How to Identify and Analyze Multiple Order Poles

Identifying multiple order poles involves examining the function’s behavior near the singularity. Here’s a step-by-step process:
- Step 1: Factorize the denominator of the function.
- Step 2: Determine the multiplicity of each factor.
- Step 3: Use the formula for residues of multiple order poles to compute their values.
📌 Note: The residue of a pole of order is given by .
Applications of Multiple Order Poles in Real-World Scenarios

Multiple order poles aren’t just theoretical constructs; they have practical applications in fields like signal processing, electrical engineering, and quantum mechanics. For instance, they help in analyzing filter responses and solving differential equations. Understanding these poles can significantly enhance your problem-solving skills in technical disciplines. (signal processing, electrical engineering, quantum mechanics)
Checklist for Mastering Multiple Order Poles
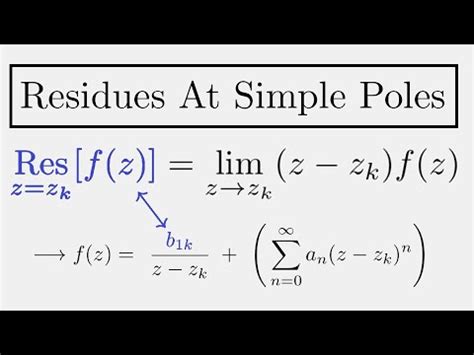
To solidify your understanding, follow this checklist:
- Review the basics of complex analysis and poles.
- Practice identifying poles in various functions.
- Apply residue formulas to compute integrals involving multiple order poles.
- Explore real-world applications to see the concept in action.
Mastering multiple order poles in complex analysis opens doors to advanced mathematical and scientific applications. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you’ll gain a solid foundation in identifying, analyzing, and applying these concepts. Whether you’re a student or a professional, this knowledge will prove invaluable in your academic or career pursuits. Keep practicing, and soon, multiple order poles will be second nature to you. (complex analysis, multiple order poles, residue calculus)
What is a multiple order pole in complex analysis?
+
A multiple order pole is a singularity of a function where the function behaves like 0)^n} with .
How do you calculate the residue of a multiple order pole?
+
The residue is calculated using the formula {z \to z_0} \frac{d^{n-1}}{dz^{n-1}} \left( (z - z_0)^n f(z) \right).
Where are multiple order poles applied in real life?
+
They are applied in signal processing, electrical engineering, and quantum mechanics for analyzing functions and solving equations.