Understanding Orbit 32 Degree Inclination: Key Facts and Insights
Understanding the concept of a 32-degree inclination orbit is crucial for anyone interested in satellite technology, space missions, or astronomy. This specific orbital inclination plays a significant role in determining a satellite’s coverage area, visibility, and operational efficiency. Whether you’re a space enthusiast or a professional in the aerospace industry, this guide will provide you with key facts and insights into the 32-degree inclination orbit.
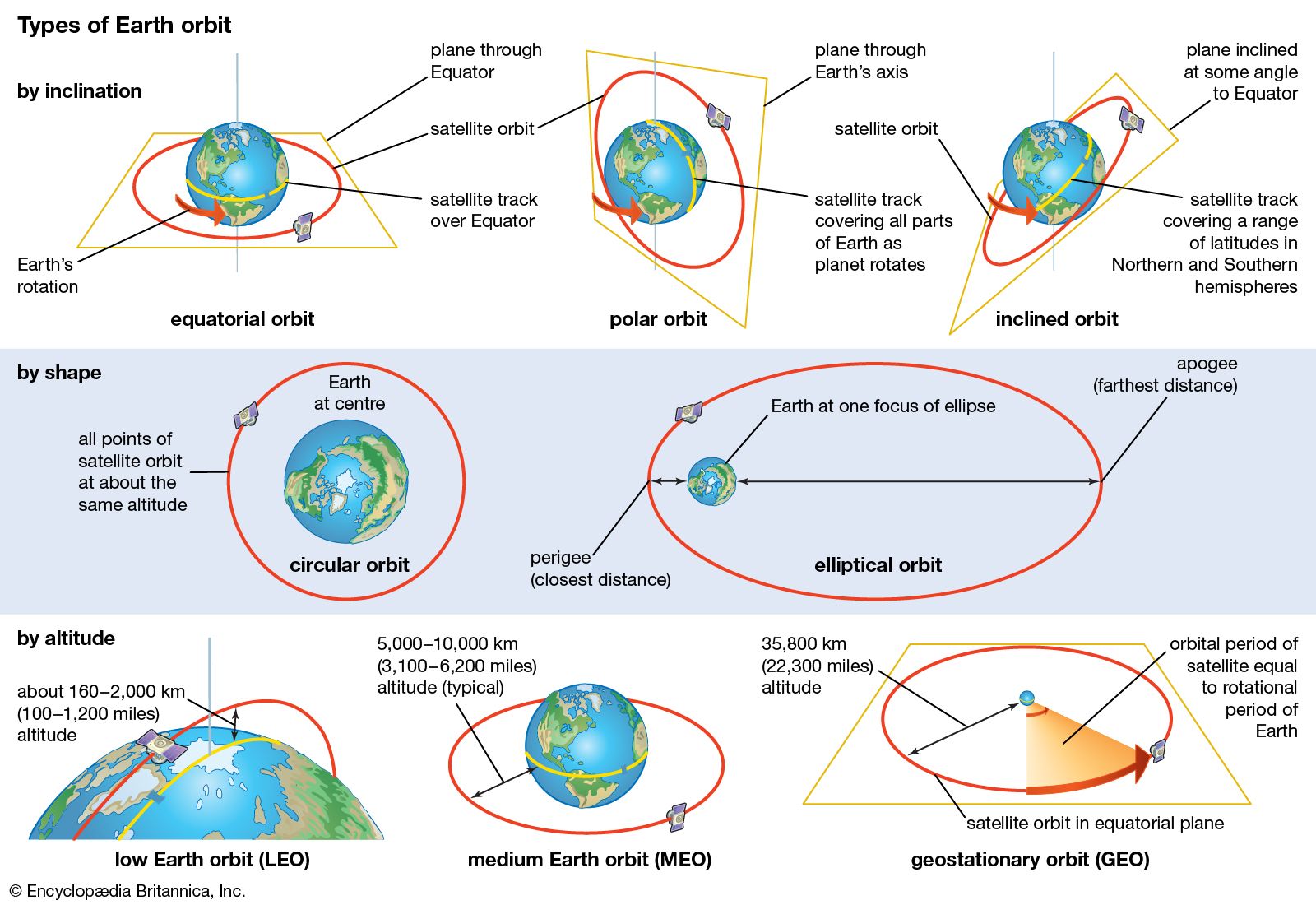
What is Orbital Inclination?
Orbital inclination refers to the angle between a satellite’s orbital plane and the Earth’s equatorial plane. A 32-degree inclination orbit means the satellite’s path is tilted 32 degrees relative to the equator. This angle is not arbitrary; it is carefully chosen to balance coverage, energy efficiency, and mission objectives.
💡 Note: Orbital inclination directly impacts a satellite's ability to cover specific regions on Earth.
Why 32 Degrees? Key Advantages

The 32-degree inclination orbit offers several benefits, making it a popular choice for various satellite missions:
- Balanced Coverage: It provides a good compromise between equatorial and polar orbits, allowing satellites to cover mid-latitude regions effectively.
- Energy Efficiency: This inclination reduces the need for frequent orbital adjustments, conserving fuel.
- Visibility: Satellites in this orbit are visible from a wide range of latitudes, enhancing their utility for communication and observation purposes.
Applications of 32-Degree Inclination Orbits
Satellites in 32-degree inclination orbits are used for diverse applications, including:
- Weather Monitoring: Tracking weather patterns in mid-latitude regions.
- Communication: Providing coverage for regions that are not served by geostationary satellites.
- Earth Observation: Capturing detailed images of specific areas for scientific research.
| Application | Benefit of 32-Degree Inclination |
|---|---|
| Weather Monitoring | Covers mid-latitude weather systems effectively |
| Communication | Extends coverage to underserved regions |
| Earth Observation | High-resolution imaging of targeted areas |
Challenges of 32-Degree Inclination Orbits
While advantageous, 32-degree inclination orbits come with challenges:
- Limited Polar Coverage: Satellites in this orbit cannot observe polar regions effectively.
- Orbital Maintenance: Periodic adjustments are required to maintain the desired inclination.
⚠️ Note: Regular monitoring is essential to ensure satellites remain within their intended orbit.
Checklist for Understanding 32-Degree Inclination Orbits
To summarize, here’s a quick checklist of key points:
- Definition: Understand that 32-degree inclination refers to the tilt of a satellite’s orbit relative to the equator.
- Advantages: Recognize the benefits of balanced coverage, energy efficiency, and visibility.
- Applications: Identify common uses in weather monitoring, communication, and Earth observation.
- Challenges: Be aware of limitations like limited polar coverage and maintenance requirements.
For those looking to optimize satellite missions or invest in space technology, understanding the 32-degree inclination orbit is essential. Its unique characteristics make it a versatile choice for a wide range of applications, from scientific research to commercial communication.
What is orbital inclination?
+Orbital inclination is the angle between a satellite's orbital plane and the Earth's equatorial plane.
Why is a 32-degree inclination orbit popular?
+It offers balanced coverage, energy efficiency, and visibility for mid-latitude regions.
What are the main applications of 32-degree inclination orbits?
+They are used for weather monitoring, communication, and Earth observation.
satellite technology, space missions, orbital mechanics, orbit 32 degree inclination,key facts and insights,key facts and insights,etc.