Unraveling the Parasite Definition: An Odyssey Through Biology
The concept of a parasite has fascinated and perplexed biologists for centuries. These organisms, often living at the expense of their hosts, play a critical role in ecosystems and human health. But what exactly defines a parasite? In this odyssey through biology, we’ll unravel the parasite definition, explore their types, and understand their impact on life as we know it.
What is a Parasite? Understanding the Basics

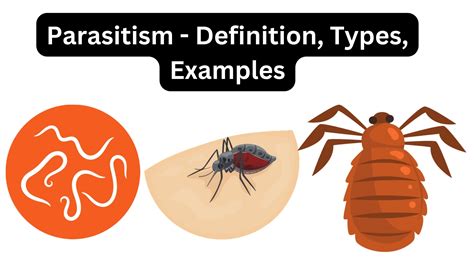
A parasite is an organism that lives on or inside another organism, known as the host, and benefits by deriving nutrients at the host’s expense. This relationship is often harmful to the host, though not always lethal. Parasites can range from microscopic protozoa to larger organisms like worms.
Key Characteristics of Parasites
- Dependence on a Host: Parasites rely on hosts for survival.
- Harmful Interaction: They typically cause harm, though some relationships are symbiotic.
- Diverse Forms: Parasites can be single-celled, multicellular, or even viral.
📌 Note: Not all organisms that live on hosts are parasites; some, like commensal bacteria, do not harm their hosts.
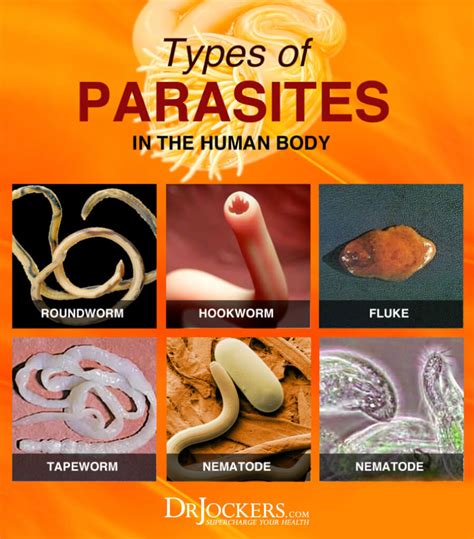
Types of Parasites: A Closer Look

Parasites are classified based on their life cycles, hosts, and modes of transmission. Understanding these types helps in studying their behavior and impact.
1. Ectoparasites vs. Endoparasites
- Ectoparasites: Live on the host’s surface (e.g., ticks, lice).
- Endoparasites: Live inside the host’s body (e.g., tapeworms, malaria parasites).
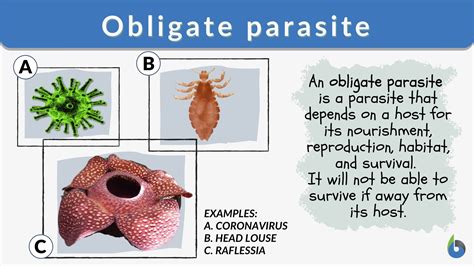
2. Obligate vs. Facultative Parasites
- Obligate Parasites: Cannot survive without a host (e.g., Plasmodium).
- Facultative Parasites: Can live independently but choose to parasitize (e.g., certain fungi).
| Type | Example | Impact on Host |
|---|---|---|
| Ectoparasite | Lice | Skin irritation, anemia |
| Endoparasite | Tapeworm | Nutrient depletion, intestinal blockage |

The Role of Parasites in Ecosystems
Parasites are not just nuisances; they play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance. By regulating host populations, they prevent overpopulation and ensure biodiversity.
Parasites and Biodiversity
- Population Control: Parasites keep host populations in check.
- Coevolution: Hosts and parasites evolve together, driving genetic diversity.
Parasites in Human Health
While some parasites cause diseases like malaria and schistosomiasis, others have medical applications. For instance, certain parasites are used in treating autoimmune disorders.
💡 Note: Research into parasitic therapies is an emerging field in medicine.
How to Protect Against Parasitic Infections
Preventing parasitic infections involves understanding their transmission and adopting protective measures.
Prevention Tips
- Hygiene: Wash hands regularly and cook food thoroughly.
- Awareness: Avoid contaminated water and practice safe travel habits.
- Medical Checks: Regular screenings for at-risk individuals.
Treatment Options
- Antiparasitic Drugs: Medications like albendazole and ivermectin.
- Lifestyle Changes: Strengthening immunity through diet and exercise.
Final Thoughts: The Complex World of Parasites

Parasites, though often viewed negatively, are integral to the web of life. From regulating ecosystems to inspiring medical breakthroughs, their impact is profound. By understanding their biology, we can better coexist with these organisms and mitigate their harmful effects.
What is the simplest definition of a parasite?
+A parasite is an organism that lives on or inside a host, benefiting at the host’s expense.
Can parasites be beneficial to humans?
+Yes, some parasites are used in medical treatments, such as helminth therapy for autoimmune diseases.
How do parasites affect ecosystems?
+Parasites regulate host populations, prevent overpopulation, and contribute to biodiversity.
parasite definition,types of parasites,parasites in ecosystems,parasitic infections,parasite prevention,parasite treatment,helminth therapy,autoimmune diseases,ecological balance,biodiversity,host-parasite relationship,ectoparasites,endoparasites,obligate parasites,facultative parasites,antiparasitic drugs,parasite biology,medical applications of parasites,parasite research,parasite impact on health.