Picture of Quota in Social Studies Explained

<!DOCTYPE html>
Understanding the concept of quota in social studies is essential for grasping how societies manage resources, opportunities, and representation. Whether you’re a student, educator, or simply curious about social systems, this guide breaks down the complexities of quotas into digestible insights. From historical contexts to modern applications, we’ll explore how quotas shape politics, economics, and social justice. Let’s dive into the picture of quota in social studies and uncover its significance in today’s world.
What is a Quota in Social Studies?

A quota in social studies refers to a fixed share or proportion assigned to a particular group, often to ensure fairness or representation. This concept is widely used in areas like politics, economics, and education. For instance, affirmative action programs often employ quotas to increase the representation of underrepresented groups. Understanding quotas helps us analyze how societies address inequality and allocate resources.
📌 Note: Quotas are not always universally accepted and can spark debates about fairness and meritocracy.
Historical Context of Quotas
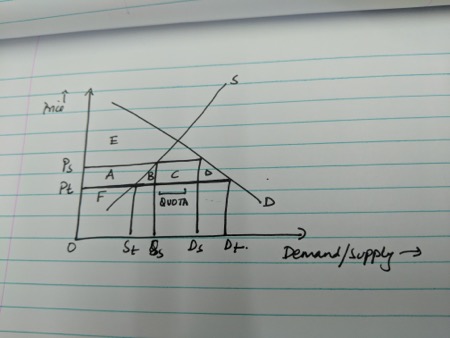
Quotas have a rich history, often emerging as responses to systemic inequalities. For example, the Indian caste system historically used quotas to reserve positions for lower castes. Similarly, gender quotas have been implemented globally to increase women’s representation in leadership roles. Exploring these historical examples provides insight into the evolution of quota systems and their impact on social structures.
Types of Quotas in Social Studies

Quotas can be categorized into various types based on their purpose and application:
- Political Quotas: Ensure representation of minority groups in government.
- Economic Quotas: Regulate trade or limit production to protect domestic industries.
- Educational Quotas: Reserve seats in institutions for underrepresented communities.
Each type serves a unique purpose, reflecting the diverse ways societies address inequality.
Pros and Cons of Quota Systems

Advantages of Quotas
Quotas promote diversity and inclusivity by providing opportunities to marginalized groups. They can also accelerate social change by breaking down barriers to representation. For example, gender quotas in corporate boards have led to increased female leadership globally.
Disadvantages of Quotas
Critics argue that quotas can lead to reverse discrimination or undermine meritocracy. They may also create resentment among groups not benefiting from the quota system. Balancing these pros and cons is crucial for effective policy-making.
Quota Systems Around the World

Different countries implement quotas in unique ways. Here’s a glimpse:
| Country | Type of Quota | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| India | Caste-based | Reserve jobs and education for lower castes |
| Rwanda | Gender-based | Ensure women’s representation in parliament |
| European Union | Trade-based | Limit imports to protect domestic industries |

These examples highlight the global relevance of quotas in addressing social and economic challenges.
How to Analyze Quotas in Social Studies
Analyzing quotas requires a critical approach. Consider the following steps:
- Identify the purpose of the quota system.
- Examine its impact on affected groups.
- Evaluate public perception and controversies.
- Compare it with alternative policies.
This analytical framework helps in understanding the effectiveness and implications of quota systems.
Checklist for Understanding Quotas
Use this checklist to deepen your understanding of quotas:
- Learn the definition of quotas in social studies.
- Explore historical examples of quota systems.
- Identify different types of quotas and their purposes.
- Analyze the pros and cons of quota systems.
- Study global examples of quota implementations.
Quotas play a pivotal role in shaping social, political, and economic landscapes. By understanding their historical context, types, and global applications, we can better evaluate their impact on society. Whether you’re studying social studies or simply curious about how quotas work, this guide provides a comprehensive overview to enhance your knowledge. Remember, quotas are tools for change, but their effectiveness depends on thoughtful implementation and continuous evaluation. (social justice, affirmative action, diversity and inclusion)
What is the main purpose of a quota in social studies?
+The main purpose of a quota is to ensure fairness and representation by allocating a fixed share to specific groups, often addressing historical or systemic inequalities.
Are quotas the same as affirmative action?
+While related, quotas and affirmative action differ. Quotas set specific numbers or percentages, whereas affirmative action focuses on broader policies to promote diversity without fixed targets.
What are some criticisms of quota systems?
+Common criticisms include potential reverse discrimination, undermining meritocracy, and creating resentment among groups not benefiting from the quota system.