Understanding Pulse Jitter and Phase Noise: Key Concepts
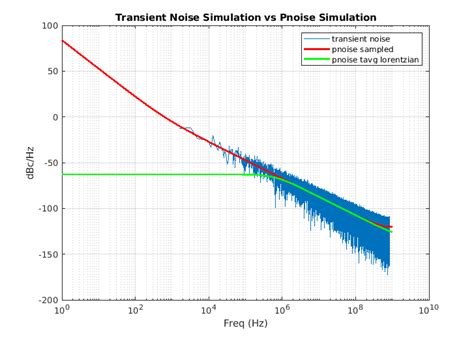
In the world of electronics and signal processing, pulse jitter and phase noise are critical concepts that can significantly impact the performance of your systems. Whether you’re designing a high-speed communication system or working with precision timing applications, understanding these phenomena is essential. This post will break down the key concepts, their implications, and how to mitigate their effects, tailored for both informational and commercial audiences.
What is Pulse Jitter?
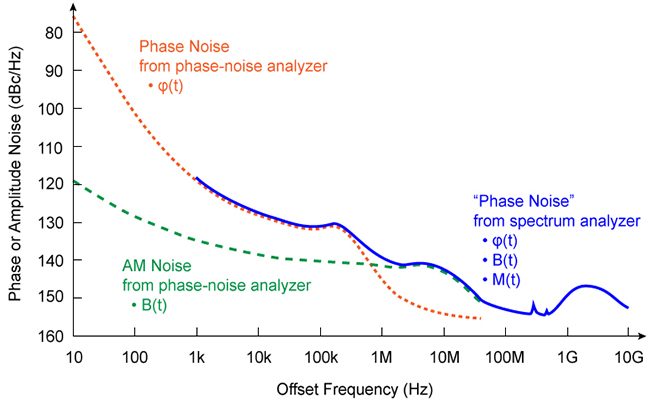
Pulse jitter refers to the deviation in the timing of a pulse from its ideal position. It is a measure of the uncertainty in the arrival time of a signal edge. Jitter can be caused by various factors, including noise, temperature fluctuations, and component variations.
Types of Jitter
- Random Jitter: Unpredictable variations caused by noise.
- Deterministic Jitter: Predictable variations caused by specific sources like power supply noise or EMI.
📌 Note: Understanding the type of jitter is crucial for selecting the right mitigation strategies.
What is Phase Noise?

Phase noise is the rapid, short-term, random fluctuations in the phase of a signal. It is closely related to jitter but focuses on the frequency domain. Phase noise is typically measured in decibels relative to the carrier power (dBc/Hz).
Causes of Phase Noise
- Oscillator Imperfections: Inadequate design or low-quality components.
- External Interference: EMI or power supply noise.
📌 Note: Phase noise directly affects the stability and reliability of communication systems.
Impact on Systems
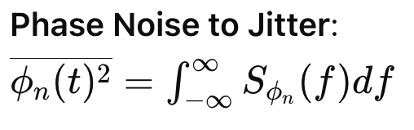
Both pulse jitter and phase noise can degrade system performance, leading to:
- Bit Errors: In digital communication systems.
- Timing Errors: In precision timing applications.
- Signal Degradation: In analog systems.
Mitigation Strategies

Reducing Jitter
- Use High-Quality Components: Invest in low-jitter oscillators and clocks.
- Improve Power Supply: Use regulated power supplies with low noise.
- Shielding: Minimize EMI with proper shielding techniques.
Minimizing Phase Noise
- Select Low-Phase-Noise Oscillators: Choose components designed for stability.
- Optimize PCB Design: Ensure proper grounding and signal routing.
- Filter Noise: Implement filters to reduce external interference.
Key Takeaways

- Pulse Jitter and phase noise are critical parameters in signal integrity.
- Understanding their causes and effects is essential for system optimization.
- Mitigation strategies include using high-quality components, improving power supplies, and optimizing design.
What is the difference between jitter and phase noise?
+Jitter refers to timing deviations in the time domain, while phase noise measures frequency fluctuations in the frequency domain.
How does jitter affect communication systems?
+Jitter can cause bit errors and signal degradation, leading to reduced system reliability and performance.
What are the best practices for reducing phase noise?
+Use low-phase-noise oscillators, optimize PCB design, and implement noise filtering techniques.
By mastering these concepts and implementing effective strategies, you can ensure the reliability and performance of your systems, whether for informational or commercial applications. (signal integrity,electronics design,communication systems)



