Mastering Randomization Tests: Theory & Real-World Apps
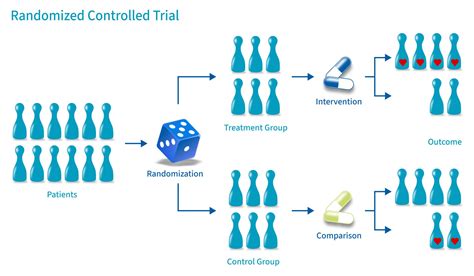
Randomization tests, also known as permutation tests, are a powerful statistical tool that allows researchers and data analysts to draw robust conclusions without relying on strict assumptions about the data distribution. Unlike traditional parametric tests, randomization tests are non-parametric, making them versatile and applicable in a wide range of scenarios. Whether you’re a data scientist, researcher, or statistician, mastering randomization tests can significantly enhance your analytical toolkit. This blog explores the theory behind randomization tests, their real-world applications, and provides actionable insights to help you implement them effectively. (randomization tests, non-parametric tests, statistical analysis)
Understanding Randomization Tests: The Basics

Randomization tests are based on the idea of reshuffling data to assess the likelihood of observing a particular outcome under the null hypothesis. By randomly reassigning labels or group memberships, these tests create a distribution of possible outcomes, allowing you to determine the statistical significance of your results. This approach is particularly useful when dealing with small sample sizes or non-normal data distributions. (statistical significance, null hypothesis, data reshuffling)
Key Concepts in Randomization Tests
- Null Hypothesis: The assumption that there is no significant difference between groups or variables.
- Permutation: The process of rearranging data to simulate all possible outcomes under the null hypothesis.
- Test Statistic: The metric used to compare observed and permuted data (e.g., mean difference, correlation coefficient).
📊 Note: Randomization tests are especially valuable when traditional tests like t-tests or ANOVA may not be appropriate due to violations of assumptions.
How to Perform a Randomization Test: Step-by-Step Guide
Performing a randomization test involves several straightforward steps. Here’s a concise guide to help you get started:
- Define the Null Hypothesis: Clearly state the assumption you’re testing.
- Calculate the Test Statistic: Compute the observed value of your test statistic from the original data.
- Permute the Data: Randomly reassign group labels and recalculate the test statistic for each permutation.
- Generate the Null Distribution: Repeat the permutation process multiple times to create a distribution of test statistics.
- Determine p-value: Calculate the proportion of permuted statistics more extreme than the observed value.
Tools for Randomization Tests
- Python: Use libraries like
scipy.statsorstatsmodels.
- R: Leverage functions like
shuffle()andreplicate().
- Excel: Manually permute data or use add-ins for automation.
| Tool | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Python | Highly customizable, scalable | Requires programming knowledge |
| R | Extensive statistical functions | Steep learning curve |
| Excel | User-friendly, no coding required | Limited for large datasets |

Real-World Applications of Randomization Tests
Randomization tests are not just theoretical constructs; they have practical applications across various fields. Here are some examples:
- Biomedical Research: Comparing treatment outcomes in clinical trials.
- Social Sciences: Analyzing survey data with small sample sizes.
- A/B Testing: Evaluating the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
- Environmental Studies: Assessing the impact of interventions on ecosystems.
Case Study: A/B Testing in E-Commerce
In e-commerce, randomization tests can help determine whether changes to a website (e.g., button color, layout) lead to a significant increase in conversions. By randomly assigning users to control and experimental groups, businesses can avoid biases and make data-driven decisions. (A/B testing, e-commerce optimization, conversion rate)
Checklist for Implementing Randomization Tests

To ensure successful implementation, follow this checklist:
- Define the research question clearly.
- Verify that the data meets the criteria for randomization tests.
- Choose an appropriate test statistic.
- Perform a sufficient number of permutations.
- Interpret the p-value in the context of the study.
🔍 Note: Always validate your results with multiple permutations to ensure robustness.
Randomization tests offer a flexible and reliable approach to statistical inference, making them an essential tool for anyone working with data. By understanding their theory and applications, you can tackle complex problems with confidence. Whether you’re analyzing small datasets or conducting large-scale experiments, randomization tests provide a solid foundation for drawing meaningful conclusions. (statistical inference, data analysis, experimental design)
What is the main advantage of randomization tests?
+
Randomization tests do not rely on assumptions about data distribution, making them suitable for a wide range of datasets.
Can randomization tests be used for large datasets?
+
Yes, but computational resources may be required for a large number of permutations.
How do randomization tests differ from t-tests?
+
T-tests assume normality and equal variance, while randomization tests do not require these assumptions.


