Selective Sliced Wasserstein Distance Explained Simply
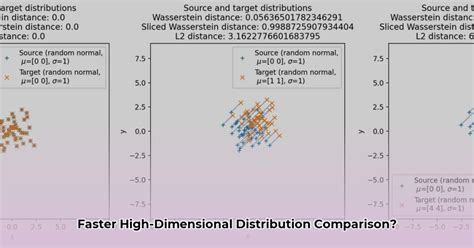
The Selective Sliced Wasserstein Distance (SSWD) is a powerful metric used in machine learning and data science to compare probability distributions. Unlike traditional methods, SSWD focuses on specific slices or regions of the data, making it particularly useful for tasks like generative modeling, domain adaptation, and anomaly detection. By selectively comparing parts of distributions, SSWD provides a more nuanced understanding of differences, especially in high-dimensional spaces. This blog will break down SSWD in simple terms, explain its applications, and provide actionable insights for both informational and commercial audiences.
What is Selective Sliced Wasserstein Distance?

The Wasserstein Distance measures the difference between two probability distributions by calculating the minimum “cost” of transforming one distribution into another. However, Selective Sliced Wasserstein Distance takes this a step further by focusing on specific slices or projections of the data. This approach reduces computational complexity and highlights differences in critical regions, making it ideal for complex datasets.
Key Components of SSWD
- Slicing: Data is projected onto one-dimensional subspaces, simplifying comparisons.
- Selectivity: Only specific slices are considered, ignoring less relevant regions.
- Wasserstein Metric: Measures the “effort” required to align distributions in the selected slices.
📌 Note: SSWD is particularly effective in high-dimensional spaces where traditional methods struggle.
Why Use Selective Sliced Wasserstein Distance?
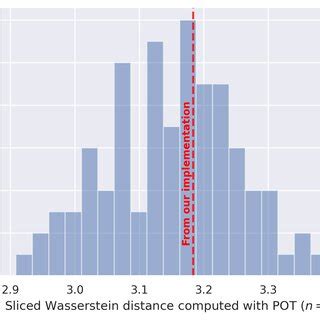
Advantages Over Traditional Metrics
- Reduced Complexity: By focusing on slices, SSWD avoids the curse of dimensionality.
- Interpretability: Highlights differences in specific regions, aiding in root-cause analysis.
- Scalability: Efficient for large datasets and complex distributions.
Applications of SSWD
- Generative Modeling: Evaluate the quality of generated data by comparing slices.
- Domain Adaptation: Identify and align critical regions between source and target domains.
- Anomaly Detection: Detect deviations in specific slices of the data distribution.
How to Implement Selective Sliced Wasserstein Distance
Step-by-Step Guide
- Data Preparation: Normalize and preprocess your dataset.
- Slicing: Project data onto one-dimensional subspaces (e.g., random directions).
- Selectivity: Choose slices of interest based on domain knowledge or automated methods.
- Computation: Calculate the Wasserstein distance for the selected slices.
- Interpretation: Analyze results to understand distribution differences.
📌 Note: Use libraries like PyTorch or TensorFlow for efficient implementation.
Tools and Libraries
- POT (Python Optimal Transport): A dedicated library for Wasserstein distance calculations.
- Scikit-learn: For data preprocessing and slicing.
- Custom Scripts: Tailor implementations for specific use cases.
Practical Tips for Using SSWD
- Choose Slices Wisely: Focus on regions relevant to your problem.
- Balance Selectivity: Avoid overfitting by considering enough slices.
- Visualize Results: Use heatmaps or plots to interpret slice-wise differences.
SSWD in Commercial Applications

For businesses, SSWD offers actionable insights into data distributions, enabling:
- Improved Model Performance: Fine-tune generative models for better outputs.
- Efficient Domain Adaptation: Reduce costs in cross-domain applications.
- Robust Anomaly Detection: Identify anomalies in critical regions of data.
By leveraging SSWD, companies can enhance decision-making and optimize processes, especially in data-intensive industries like finance, healthcare, and manufacturing.
Summarizing SSWD: Key Takeaways
- SSWD simplifies distribution comparisons by focusing on specific slices.
- It’s efficient, interpretable, and scalable for high-dimensional data.
- Applications span generative modeling, domain adaptation, and anomaly detection.
Checklist for Implementing SSWD
- [ ] Preprocess and normalize your dataset.
- [ ] Project data onto one-dimensional slices.
- [ ] Select relevant slices for comparison.
- [ ] Compute Wasserstein distance for selected slices.
- [ ] Interpret results and visualize differences.
What is the main advantage of SSWD over traditional Wasserstein distance?
+SSWD reduces computational complexity by focusing on specific slices of the data, making it more efficient for high-dimensional datasets.
Can SSWD be used for time-series data?
+Yes, SSWD can be applied to time-series data by slicing along relevant dimensions, such as time intervals or feature subspaces.
How do I choose the right slices for SSWD?
+Use domain knowledge or automated methods like PCA to identify critical regions in your data distribution.
In wrapping up, Selective Sliced Wasserstein Distance is a versatile and efficient tool for comparing probability distributions. By focusing on specific slices, it offers deeper insights into data differences, making it invaluable for both research and commercial applications. Whether you’re improving generative models or detecting anomalies, SSWD provides a scalable and interpretable solution for complex datasets.
Related Keywords: Wasserstein Distance, Generative Modeling, Domain Adaptation, Anomaly Detection, High-Dimensional Data