Small Courtroom Dynamics: Understanding Labeled Roles and Functions
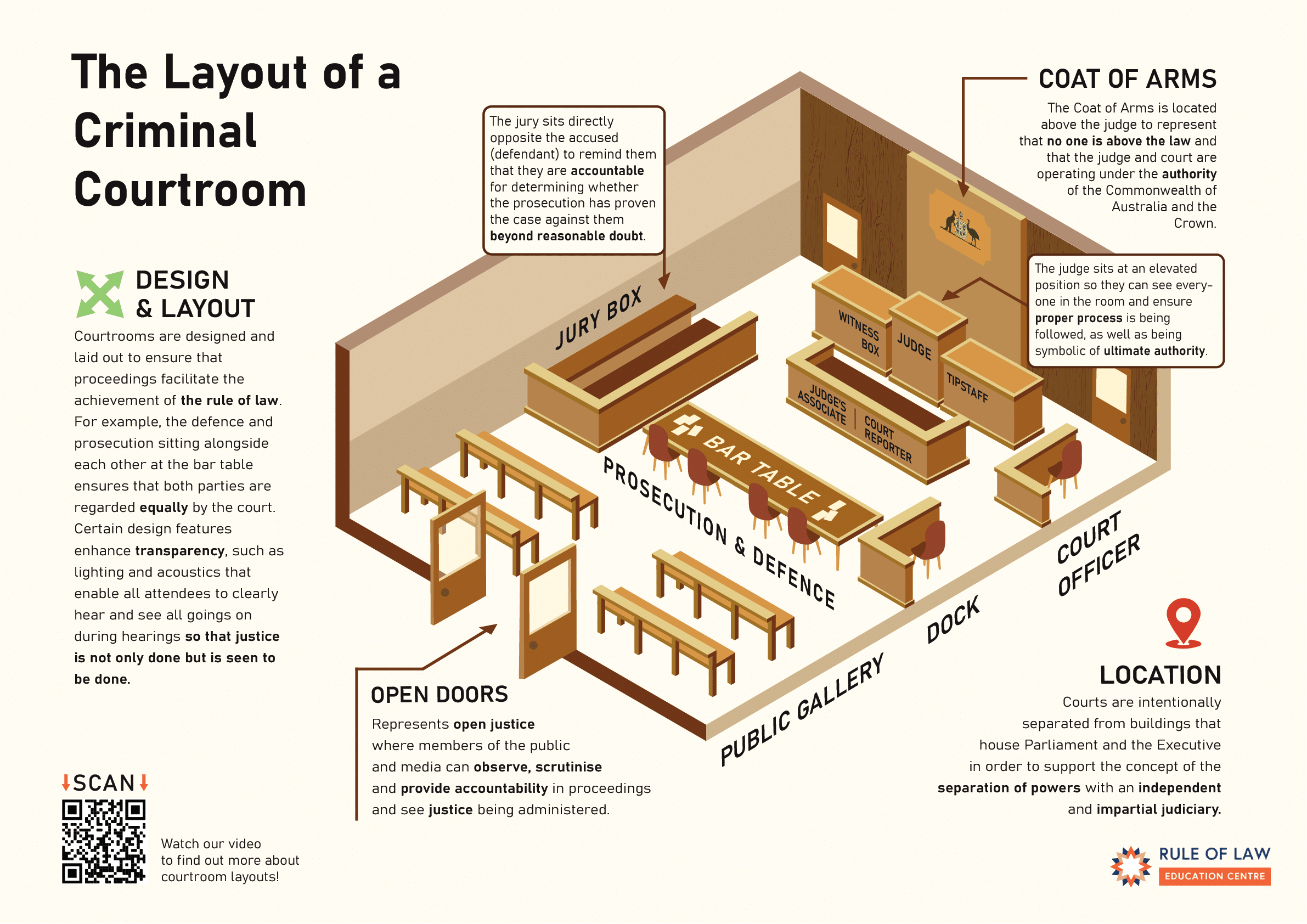
Understanding Small Courtroom Dynamics: A Guide to Key Roles and Functions
Navigating the intricacies of a courtroom can be daunting, especially for those unfamiliar with its structure and procedures. This guide delves into the small courtroom dynamics, shedding light on the labeled roles and functions of key participants. Whether you’re a legal professional, a student, or simply curious about the legal system, understanding these dynamics is crucial. (Courtroom Procedures, Legal System, Roles in Court)
The Players in the Legal Arena
A small courtroom typically involves a judge, attorneys, witnesses, court reporters, and sometimes a jury. Each role is vital to the fair and efficient administration of justice. (Courtroom Roles, Judge, Attorneys, Witnesses, Court Reporter, Jury)
The Judge: The Guardian of Justice
The judge presides over the proceedings, ensuring fairness and adherence to legal principles. They make rulings on evidence, interpret laws, and ultimately deliver the verdict or sentence.
Attorneys: Advocates and Legal Experts
Prosecutors represent the state or government, presenting evidence to prove the defendant’s guilt. Defense attorneys advocate for the accused, challenging the prosecution’s case and protecting their client’s rights. (Prosecutor, Defense Attorney, Legal Advocacy)
Witnesses: Providing Crucial Testimony
Witnesses provide firsthand accounts of events relevant to the case. Their testimony can be pivotal in determining the outcome.
Court Reporters: The Record Keepers
Court reporters create a verbatim transcript of everything spoken during the trial, ensuring an accurate record for future reference.
The Jury: The Voice of the Community
In some cases, a jury of peers decides the verdict based on the evidence presented. They represent the community’s perspective and ensure a fair trial by impartial individuals. (Jury Trial, Verdict, Impartiality)
Understanding the Flow of a Trial
A typical trial follows a structured sequence:
- Opening Statements: Attorneys outline their case theories. (Opening Statements, Case Theory)
- Witness Testimony and Cross-Examination: Witnesses testify, and attorneys question them to elicit information and challenge credibility.
- Presentation of Evidence: Documents, objects, and other relevant materials are presented to support arguments.
- Closing Arguments: Attorneys summarize their cases and persuade the judge or jury.
- Jury Deliberation (if applicable): Jurors discuss the evidence and reach a verdict.
- Verdict and Sentencing: The judge delivers the verdict and, if applicable, imposes a sentence.
Navigating the Courtroom: A Checklist
- Research the Courtroom Layout: Familiarize yourself with the seating arrangement and roles of each participant. (Courtroom Layout, Courtroom Etiquette)
- Dress Appropriately: Maintain a professional and respectful demeanor with attire suitable for a formal setting.
- Arrive Early: Allow ample time for security checks and finding your seat.
- Observe Courtroom Etiquette: Be respectful, avoid distractions, and follow the judge’s instructions.
- Take Notes: Jot down key points and observations for later reference.
Final Thoughts
Understanding small courtroom dynamics empowers individuals to navigate the legal system with greater confidence. By recognizing the roles and functions of key players, we can appreciate the complexities of the justice system and its commitment to fairness and impartiality. (Legal System, Justice, Fairness, Impartiality)
What is the role of a bailiff in a courtroom?
+Bailiffs maintain order in the courtroom, escort jurors, and handle exhibits.
Can I bring my phone into the courtroom?
+Check with the specific court, but generally, phones must be silenced or turned off.
What happens if I don’t understand something during the trial?
+You can ask for clarification from your attorney or the court clerk.



