Sulfuric Acid Absorption Spectrum: Key Wavelengths in nm
Understanding the sulfuric acid absorption spectrum is crucial for researchers, chemists, and industries utilizing this versatile chemical. Sulfuric acid, known for its strong acidic properties, exhibits unique interactions with light across different wavelengths, making its absorption spectrum a key area of study. This spectrum reveals how sulfuric acid absorbs electromagnetic radiation, particularly in the ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) regions. By analyzing these absorption patterns, scientists can gain insights into its molecular structure, chemical behavior, and applications in various fields.
Whether you’re a student, researcher, or industry professional, grasping the key wavelengths in nm of sulfuric acid’s absorption spectrum is essential for optimizing its use in processes like catalysis, environmental monitoring, and material synthesis. This blog post delves into the critical wavelengths, their significance, and practical applications, ensuring you have the knowledge needed to work effectively with this powerful chemical.
Key Wavelengths in the Sulfuric Acid Absorption Spectrum

Sulfuric acid’s absorption spectrum is characterized by specific wavelengths where it interacts most strongly with light. These wavelengths are primarily found in the UV and IR regions, with each range providing unique information about the molecule’s properties.
Ultraviolet (UV) Region
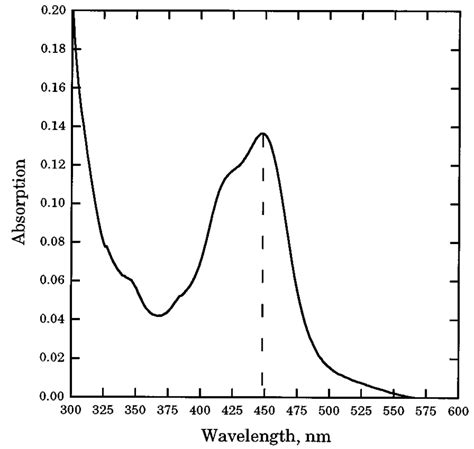
In the UV region, sulfuric acid shows absorption peaks around 200–300 nm. These wavelengths correspond to electronic transitions within the molecule, particularly involving the oxygen and sulfur atoms.
- 220 nm: A prominent peak associated with the S-O bond’s electronic excitation.
- 250 nm: Another significant absorption band related to molecular vibrations and electronic transitions.
💡 Note: UV absorption data is vital for studying sulfuric acid’s reactivity and stability under different conditions.
Infrared (IR) Region
The IR region reveals vibrational modes of sulfuric acid molecules, offering insights into bond strengths and molecular geometry. Key wavelengths include:
- 1000–1200 nm: Corresponds to O-H stretching vibrations.
- 600–800 nm: Associated with S-O stretching and bending vibrations.
These IR absorption bands are crucial for identifying sulfuric acid in analytical chemistry and environmental studies.
| Region | Wavelength (nm) | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| UV | 200–300 nm | Electronic transitions, S-O bond excitation |
| IR | 1000–1200 nm | O-H stretching vibrations |
| IR | 600–800 nm | S-O stretching and bending vibrations |

Practical Applications of Sulfuric Acid Absorption Spectrum

The absorption spectrum of sulfuric acid has wide-ranging applications across industries and research fields.
Environmental Monitoring
Sulfuric acid’s IR absorption bands are used to detect its presence in atmospheric samples, aiding in air quality assessments and pollution control.
Chemical Synthesis
Understanding its UV absorption helps optimize catalytic processes where sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst or reactant.
Material Science
The spectrum aids in analyzing sulfuric acid’s role in material degradation and surface treatments.
Checklist for Analyzing Sulfuric Acid Absorption Spectrum
- Identify key UV and IR wavelengths (200–300 nm, 1000–1200 nm, 600–800 nm).
- Use spectrophotometric tools for accurate measurements.
- Correlate absorption data with molecular structure and reactivity.
- Apply findings to relevant industrial or research applications.
The sulfuric acid absorption spectrum provides invaluable insights into its molecular behavior and applications. By focusing on key wavelengths in nm, researchers and professionals can harness its properties effectively. Whether in environmental monitoring, chemical synthesis, or material science, this knowledge is a cornerstone for innovation and problem-solving.
What are the key wavelengths in sulfuric acid’s UV absorption spectrum?
+The key UV wavelengths are around 200–300 nm, with prominent peaks at 220 nm and 250 nm, corresponding to electronic transitions.
How is sulfuric acid’s IR spectrum used in environmental studies?
+IR absorption bands (1000–1200 nm, 600–800 nm) help detect sulfuric acid in atmospheric samples, aiding pollution monitoring.
Why is the absorption spectrum important for chemical synthesis?
+It helps optimize catalytic processes by understanding sulfuric acid’s reactivity and stability under different conditions.
sulfuric acid absorption spectrum,key wavelengths in nm,UV absorption,IR absorption,chemical synthesis,environmental monitoring,material science.



