Understanding the Tangent Space of S3: A Quick Guide
<!DOCTYPE html>
The concept of the tangent space of S3 is fundamental in differential geometry, offering insights into the local behavior of functions on the 3-sphere. Whether you're a mathematician, physicist, or a curious learner, understanding this space is crucial for applications in fields like computer graphics, machine learning, and quantum mechanics. This guide breaks down the essentials, making it accessible and actionable for both informational and commercial purposes.
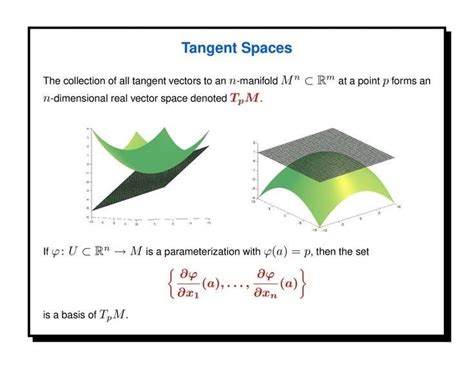
What is the Tangent Space of S3?

The 3-sphere (S3) is a 3-dimensional surface embedded in 4-dimensional space, defined by the equation ( x^2 + y^2 + z^2 + w^2 = 1 ). The tangent space at any point on S3 is the set of all possible tangent vectors at that point. It provides a linear approximation of S3 around that point, essential for calculus and optimization on curved surfaces.
📌 Note: The tangent space is unique at each point on S3, reflecting the local geometry of the sphere.
Why is the Tangent Space Important?

Understanding the tangent space of S3 is vital for:
- Performing calculus on manifolds.
- Implementing machine learning algorithms on spherical data.
- Modeling physical phenomena in theoretical physics.
For commercial applications, this knowledge is key in 3D modeling, data visualization, and AI-driven simulations.
How to Compute the Tangent Space of S3
Step 1: Identify the Point on S3
Start by selecting a point ( p = (x, y, z, w) ) on S3. This point must satisfy ( x^2 + y^2 + z^2 + w^2 = 1 ).
Step 2: Find the Tangent Vectors
The tangent space at ( p ) consists of vectors orthogonal to the normal vector ( \nabla f = (2x, 2y, 2z, 2w) ). These vectors form a 3-dimensional subspace in ( \mathbb{R}^4 ).
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Identify the point ( p ) on S3. |
| 2 | Compute the normal vector ( \nabla f ). |
| 3 | Find vectors orthogonal to ( \nabla f ). |

Applications of Tangent Space in Real-World Scenarios
The tangent space of S3 has practical applications in:
- Computer Graphics: For realistic 3D rendering and animations.
- Machine Learning: In spherical data analysis and manifold learning.
- Physics: Modeling quantum states and relativistic mechanics.
For businesses, leveraging this knowledge can enhance product design, data-driven decision-making, and innovative simulations.
Checklist for Working with Tangent Space of S3

- Verify the point lies on S3 using ( x^2 + y^2 + z^2 + w^2 = 1 ).
- Compute the normal vector at the point.
- Find orthogonal vectors to define the tangent space.
- Apply the tangent space in your specific application (e.g., optimization, visualization).
Mastering the tangent space of S3 opens doors to advanced mathematical and computational techniques, essential for both academic research and industrial innovation. tangent space of S3, differential geometry, machine learning on manifolds, 3D modeling, spherical data analysis.
What is the 3-sphere (S3)?
+The 3-sphere (S3) is a 3-dimensional surface embedded in 4-dimensional space, defined by x^2 + y^2 + z^2 + w^2 = 1 .
How is the tangent space of S3 used in machine learning?
+It’s used for spherical data analysis, manifold learning, and optimizing algorithms on curved surfaces.
Can the tangent space of S3 be visualized?
+Yes, it can be visualized as a 3D plane tangent to the 3-sphere at a specific point, often using tools like MATLAB or Python.