Understanding Entropy in 1D Solids: A Concise Guide
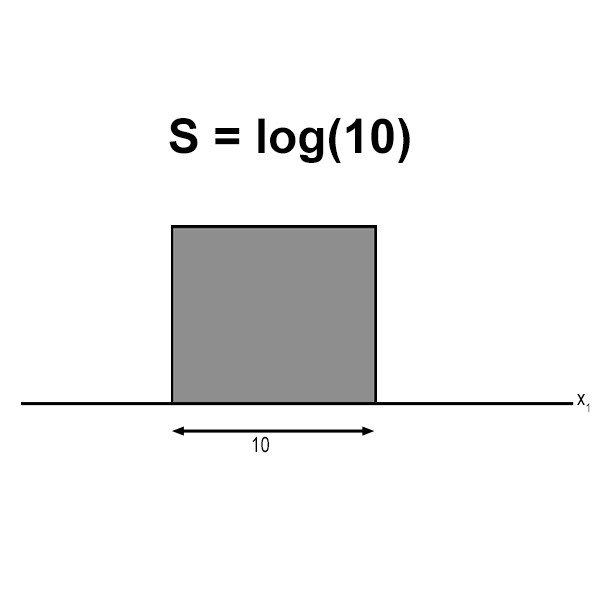
Understanding entropy in 1D solids is crucial for anyone studying materials science, physics, or engineering. Entropy, a fundamental concept in thermodynamics, measures the disorder or randomness in a system. In 1D solids, such as nanowires or chains of atoms, entropy plays a unique role due to the restricted dimensionality. This guide breaks down the concept of entropy in 1D solids, its significance, and practical applications, ensuring both informational and commercial audiences gain valuable insights.
What is Entropy in 1D Solids?
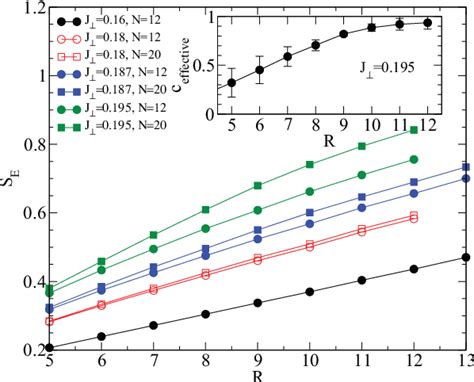
Entropy in 1D solids refers to the measure of disorder within a one-dimensional arrangement of atoms or particles. Unlike 3D systems, 1D solids exhibit unique entropy behaviors due to their limited spatial freedom. This concept is vital in understanding thermal conductivity, phase transitions, and mechanical properties of materials like carbon nanotubes or polymer chains.
📌 Note: Entropy in 1D systems is highly sensitive to temperature and structural defects, making it a critical factor in material design.
Key Factors Influencing Entropy in 1D Solids
- Temperature: Higher temperatures increase atomic vibrations, leading to greater disorder.
- Structural Defects: Imperfections like vacancies or dislocations enhance entropy by introducing randomness.
- Particle Interactions: Strong interatomic forces can reduce entropy by restricting particle movement.
Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing material performance in applications such as electronics and nanotechnology, 1D solids, entropy calculation, thermal properties.
Practical Applications of Entropy in 1D Solids
Entropy in 1D solids has significant applications across industries:
| Application | Relevance |
|---|---|
| Electronics | Improving heat dissipation in nanowire-based devices. |
| Nanotechnology | Designing high-strength materials with controlled disorder. |
| Energy Storage | Enhancing ion mobility in 1D battery electrodes. |
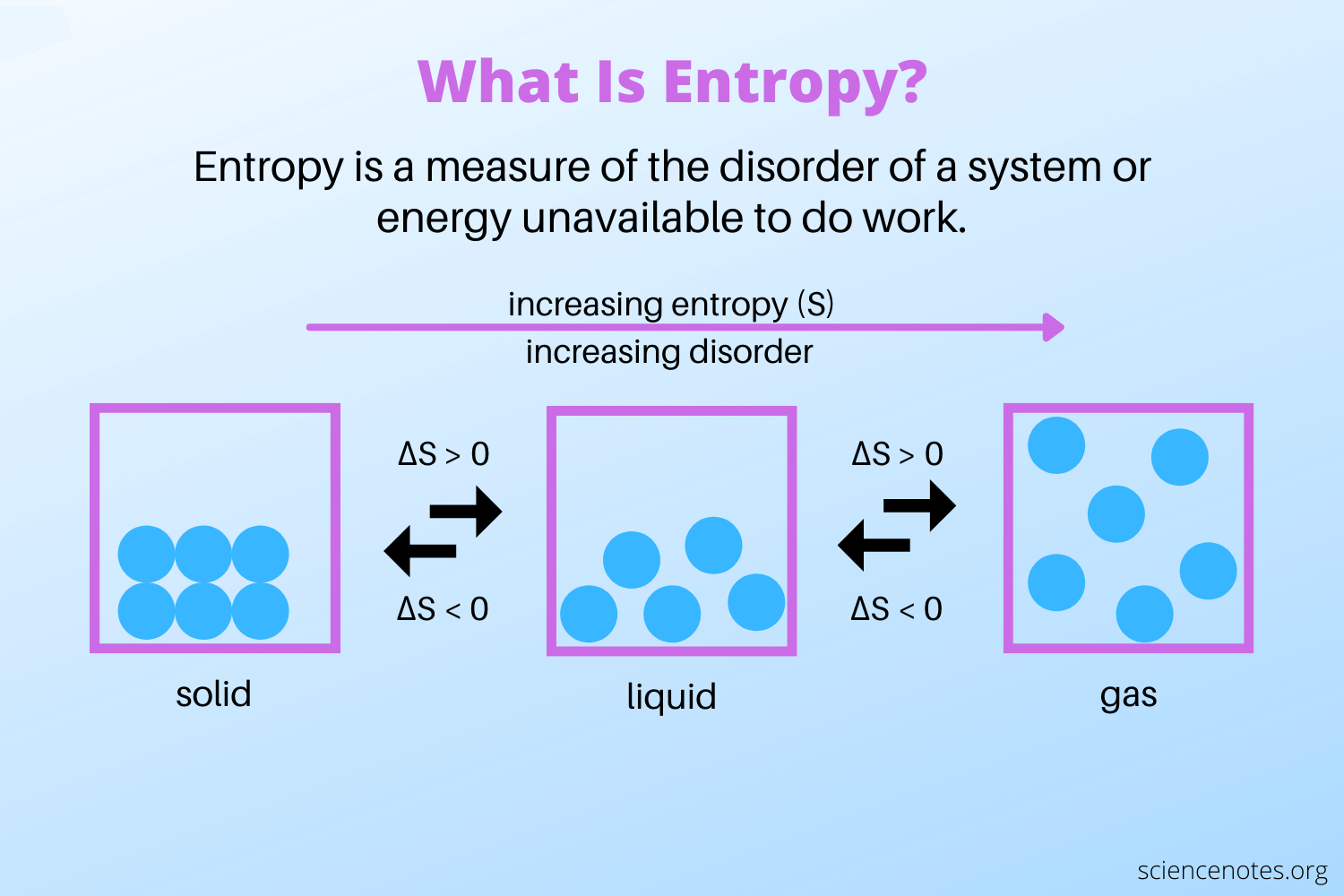
These applications highlight the importance of mastering entropy in 1D solids for innovation and efficiency, material science, thermodynamics, 1D materials.
Checklist: Mastering Entropy in 1D Solids
- Study the relationship between temperature and entropy.
- Analyze the impact of structural defects on disorder.
- Explore practical applications in your field.
- Utilize computational tools for entropy calculations.
What is the role of entropy in 1D solids?
+Entropy measures disorder in 1D solids, influencing properties like thermal conductivity and phase transitions.
How does temperature affect entropy in 1D systems?
+Higher temperatures increase atomic vibrations, leading to greater disorder and higher entropy.
Why are 1D solids important in nanotechnology?
+1D solids like nanotubes offer unique properties such as high strength and conductivity, making them ideal for nanotech applications.
In summary, entropy in 1D solids is a critical concept with far-reaching implications in material science and engineering. By understanding the factors influencing entropy and its practical applications, professionals can unlock new possibilities in technology and innovation. Whether you’re a researcher or an industry expert, mastering this topic is essential for staying ahead in the field of 1D materials, thermodynamics, entropy calculation.


