Zebrafish Axis Formation: BMP7's Crucial Role Explained
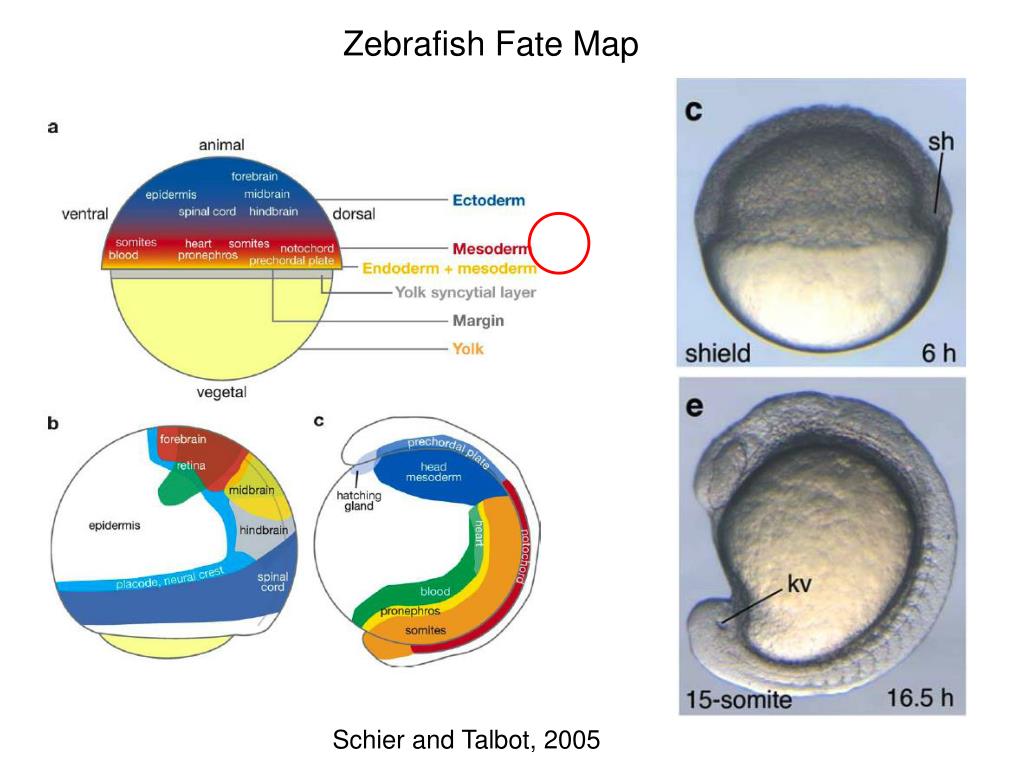
Zebrafish axis formation is a fascinating process in developmental biology, where the embryo establishes its body plan. Among the key players in this process is BMP7, a signaling molecule that plays a crucial role in patterning the dorsal-ventral axis. Understanding BMP7's function not only sheds light on zebrafish development but also provides insights into human embryology and regenerative medicine. This blog explores the significance of BMP7, its mechanisms, and its broader implications, tailored for both informational and commercial audiences. (zebrafish development, BMP signaling, embryology)
What is BMP7 and Why is it Important in Zebrafish Axis Formation?

BMP7, or Bone Morphogenetic Protein 7, is a growth factor belonging to the TGF-β superfamily. In zebrafish, BMP7 is essential for establishing the dorsal-ventral (DV) axis during early embryonic development. This axis determines the top-to-bottom organization of the embryo, influencing tissue differentiation and organ formation. Without proper BMP7 signaling, the embryo may fail to develop correctly, leading to severe developmental defects. (dorsal-ventral axis, TGF-β superfamily, tissue differentiation)
The Role of BMP7 in Dorsal-Ventral Patterning
BMP7 acts as a ventralizing factor, promoting the formation of ventral structures in the zebrafish embryo. It counteracts the dorsalizing signals from proteins like Chordin, creating a gradient that defines the DV axis. This delicate balance ensures proper cell fate specification and tissue organization. (ventralizing factor, Chordin, cell fate specification)
Mechanisms of BMP7 Signaling in Zebrafish
BMP7 exerts its effects through a complex signaling cascade involving receptors, Smad proteins, and downstream target genes. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps:
- Ligand Binding: BMP7 binds to type II and type I BMP receptors on the cell surface.
- Smad Activation: Receptor activation leads to phosphorylation of Smad1/5/8 proteins.
- Nuclear Translocation: Phosphorylated Smads form complexes with Smad4 and translocate to the nucleus.
- Gene Regulation: The Smad complex regulates the expression of genes involved in ventral development.
(BMP receptors, Smad proteins, gene regulation)
BMP7 and Its Interaction with Other Pathways
BMP7 signaling does not operate in isolation. It interacts with other pathways, such as Wnt and Nodal, to fine-tune axis formation. For instance, BMP7 modulates Wnt activity to ensure proper tissue patterning. These cross-talks highlight the complexity and precision of embryonic development. (Wnt signaling, Nodal pathway, tissue patterning)
Applications of BMP7 Research in Science and Medicine
Studying BMP7 in zebrafish has far-reaching implications, from basic research to clinical applications. Here are some key areas where BMP7 research is making an impact:
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| Developmental Biology | Understanding axis formation and tissue differentiation. |
| Regenerative Medicine | Promoting tissue repair and regeneration using BMP7-based therapies. |
| Disease Modeling | Studying BMP7-related disorders in zebrafish models. |
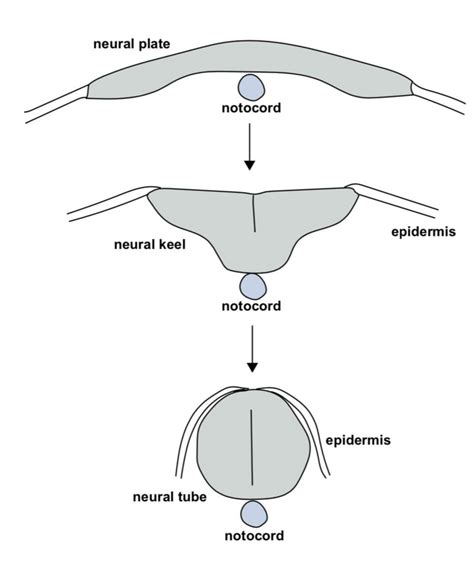
(regenerative medicine, disease modeling, tissue repair)
📌 Note: Zebrafish are ideal models for studying BMP7 due to their rapid development, transparency, and genetic tractability.
BMP7 is undeniably a key player in zebrafish axis formation, orchestrating the intricate process of dorsal-ventral patterning. Its signaling mechanisms and interactions with other pathways underscore its importance in developmental biology. For researchers and clinicians, BMP7 offers promising avenues for advancing regenerative medicine and understanding developmental disorders. Whether you're exploring zebrafish models or seeking BMP7-based solutions, this molecule’s role is both fascinating and impactful. (zebrafish models, developmental disorders, BMP7-based therapies)
What is the primary function of BMP7 in zebrafish?
+
BMP7 primarily acts as a ventralizing factor, establishing the dorsal-ventral axis during zebrafish embryonic development.
How does BMP7 signaling interact with other pathways?
+
BMP7 interacts with pathways like Wnt and Nodal to fine-tune tissue patterning and ensure proper embryonic development.
Why are zebrafish used to study BMP7?
+
Zebrafish are ideal for BMP7 research due to their rapid development, transparency, and genetic manipulability.



