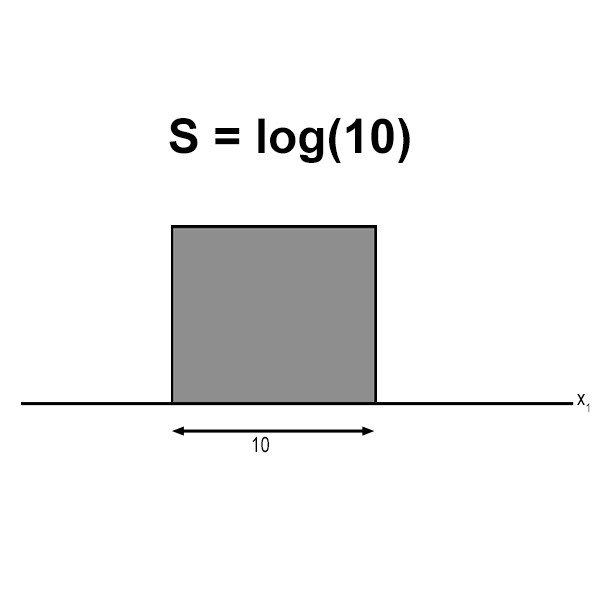Filtering in Logarithm Space: Theory Simplified

Filtering in logarithm space is a powerful technique used in signal processing, data compression, and machine learning to efficiently manage and analyze large datasets. By leveraging the properties of logarithms, this method reduces computational complexity and enhances performance, making it a valuable tool for professionals in various fields. Whether you're an engineer, data scientist, or researcher, understanding the theory behind filtering in logarithm space can unlock new possibilities for your projects. Below, we break down the concept into digestible parts, ensuring both informational and commercial audiences can grasp its importance and application.
What is Filtering in Logarithm Space?

Filtering in logarithm space involves transforming data into a logarithmic scale before applying filtering techniques. This approach is particularly useful when dealing with signals or datasets that exhibit exponential growth or decay. By working in logarithm space, you can simplify complex operations and improve the efficiency of algorithms. Common applications include audio processing, image enhancement, and financial data analysis, where logarithmic transformations help normalize data distributions.
Key Benefits of Logarithm Space Filtering
- Reduced Computational Load: Logarithmic transformations compress the dynamic range of data, making filtering operations faster.
- Improved Accuracy: Logarithm space helps mitigate issues like overflow and underflow in numerical computations.
- Enhanced Signal-to-Noise Ratio: Logarithmic filtering is effective in separating signals from noise in noisy environments.
How to Implement Filtering in Logarithm Space

Implementing filtering in logarithm space involves a series of steps, from data transformation to applying filters. Below is a simplified guide to help you get started:
Step 1: Transform Data into Logarithm Space
Begin by applying a logarithmic transformation to your dataset. Common choices include the natural logarithm (ln) or base-2 logarithm, depending on the application. This step normalizes the data and prepares it for filtering.
Step 2: Apply Filtering Techniques
Once the data is in logarithm space, apply standard filtering methods such as low-pass, high-pass, or band-pass filters. These filters can be designed using Fourier transforms or convolution operations, tailored to the specific requirements of your project.
Step 3: Inverse Transform the Filtered Data
After filtering, convert the data back to its original scale using the inverse logarithmic transformation. This step ensures the filtered output is interpretable and ready for further analysis or application.
📌 Note: Ensure your data is positive before applying logarithmic transformations, as logarithms are undefined for non-positive values.
Applications of Filtering in Logarithm Space
The versatility of filtering in logarithm space makes it applicable across multiple industries. Here are some notable examples:
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| Audio Processing | Noise reduction and dynamic range compression |
| Image Enhancement | Contrast adjustment and edge detection |
| Finance | Volatility analysis and trend filtering |
Checklist for Implementing Logarithm Space Filtering
- Verify data positivity before transformation.
- Choose the appropriate logarithmic base for your application.
- Design filters based on the transformed data characteristics.
- Test the inverse transformation for accuracy.
Filtering in logarithm space is a versatile and efficient technique that simplifies complex data processing tasks. By understanding its theory and implementation steps, you can leverage this method to enhance your projects across various domains. Whether you’re optimizing algorithms or improving data quality, logarithm space filtering offers a robust solution for modern challenges. logarithmic transformation,signal processing,data compression,
What is the main advantage of filtering in logarithm space?
+
The main advantage is reduced computational complexity, as logarithmic transformations compress the dynamic range of data, making filtering operations faster and more efficient.
Can logarithm space filtering be applied to negative data?
+
No, logarithmic transformations are undefined for non-positive values. Ensure your data is positive before applying this technique.
What are common applications of logarithm space filtering?
+
Common applications include audio processing, image enhancement, and financial data analysis, where logarithmic transformations help normalize data distributions.