Numerical Analysis of Eikonal: Key Insights Explained
<!DOCTYPE html>
The Eikonal equation is a fundamental partial differential equation in the field of wave propagation, playing a crucial role in various applications such as seismic imaging, computer graphics, and robotics. Understanding its numerical analysis is essential for accurately solving real-world problems. This blog delves into the key insights of numerical methods applied to the Eikonal equation, providing both informative and commercial perspectives for our audience.
Understanding the Eikonal Equation

The Eikonal equation describes the propagation of waves in a medium with varying properties. It is given by:
∥∇T(x)∥2 = 1/f(x), where T(x) is the traveltime, f(x) is the wave speed, and x represents the spatial coordinates. Solving this equation numerically is challenging due to its nonlinear nature and the need for high accuracy in applications like seismic imaging and path planning.
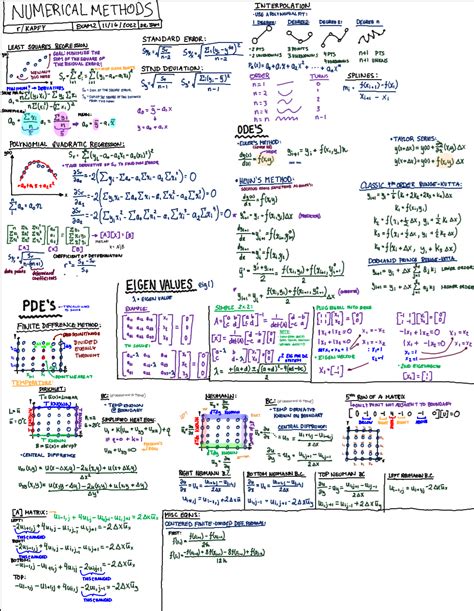
Key Numerical Methods for Solving the Eikonal Equation
Several numerical methods have been developed to tackle the Eikonal equation. Below are the most prominent ones:
- Fast Marching Method (FMM): A popular technique for its efficiency in solving the Eikonal equation on regular grids. It uses a priority queue to propagate the solution from known boundaries.
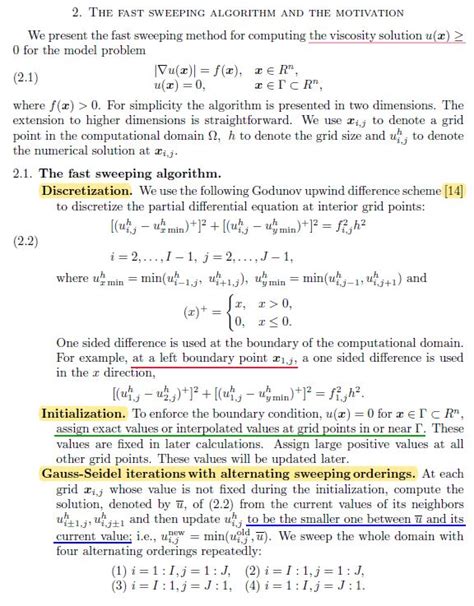
- Fast Sweeping Method (FSM): An iterative approach that alternates between sweeping in different directions to achieve convergence. It is particularly useful for unstructured grids.
- Level Set Method (LSM): Often used in conjunction with the Eikonal equation to model interfaces and fronts in evolving geometries.
📌 Note: The choice of method depends on the specific application and the nature of the grid (structured vs. unstructured).
Applications of Eikonal Equation Numerical Analysis

Seismic Imaging
In seismic exploration, the Eikonal equation is used to compute traveltimes of seismic waves, which are crucial for creating accurate subsurface images. Numerical solutions enable efficient processing of large datasets, improving the resolution of seismic surveys.
Robotics and Path Planning
For autonomous robots, the Eikonal equation helps in computing optimal paths in complex environments. Numerical methods ensure real-time computation, which is essential for dynamic obstacle avoidance.
Challenges in Numerical Analysis of Eikonal

Despite advancements, several challenges remain:
- Accuracy: Maintaining high accuracy in regions with high wave speed gradients.
- Computational Cost: Balancing efficiency and accuracy, especially for large-scale problems.
- Grid Dependency: Ensuring robustness across different grid types and resolutions.
Checklist for Implementing Eikonal Numerical Solutions

To successfully implement numerical solutions for the Eikonal equation, follow this checklist:
- Choose the appropriate numerical method based on the application.
- Ensure the grid resolution matches the problem’s requirements.
- Validate the solution against known benchmarks or analytical solutions.
- Optimize for computational efficiency, especially for real-time applications.
By mastering the numerical analysis of the Eikonal equation, professionals in fields like geophysics, computer graphics, and robotics can unlock new possibilities in their work, ensuring accurate and efficient solutions to complex problems.
What is the Eikonal equation used for?
+The Eikonal equation is used to model wave propagation in various fields, including seismic imaging, robotics, and computer graphics.
Which numerical method is best for solving the Eikonal equation?
+The choice depends on the application. The Fast Marching Method is efficient for regular grids, while the Fast Sweeping Method is better for unstructured grids.
How does the Eikonal equation apply to robotics?
+In robotics, the Eikonal equation is used for path planning, helping autonomous robots navigate complex environments efficiently.



