Savanna Birds: Carnivores, Herbivores, or Omnivores?
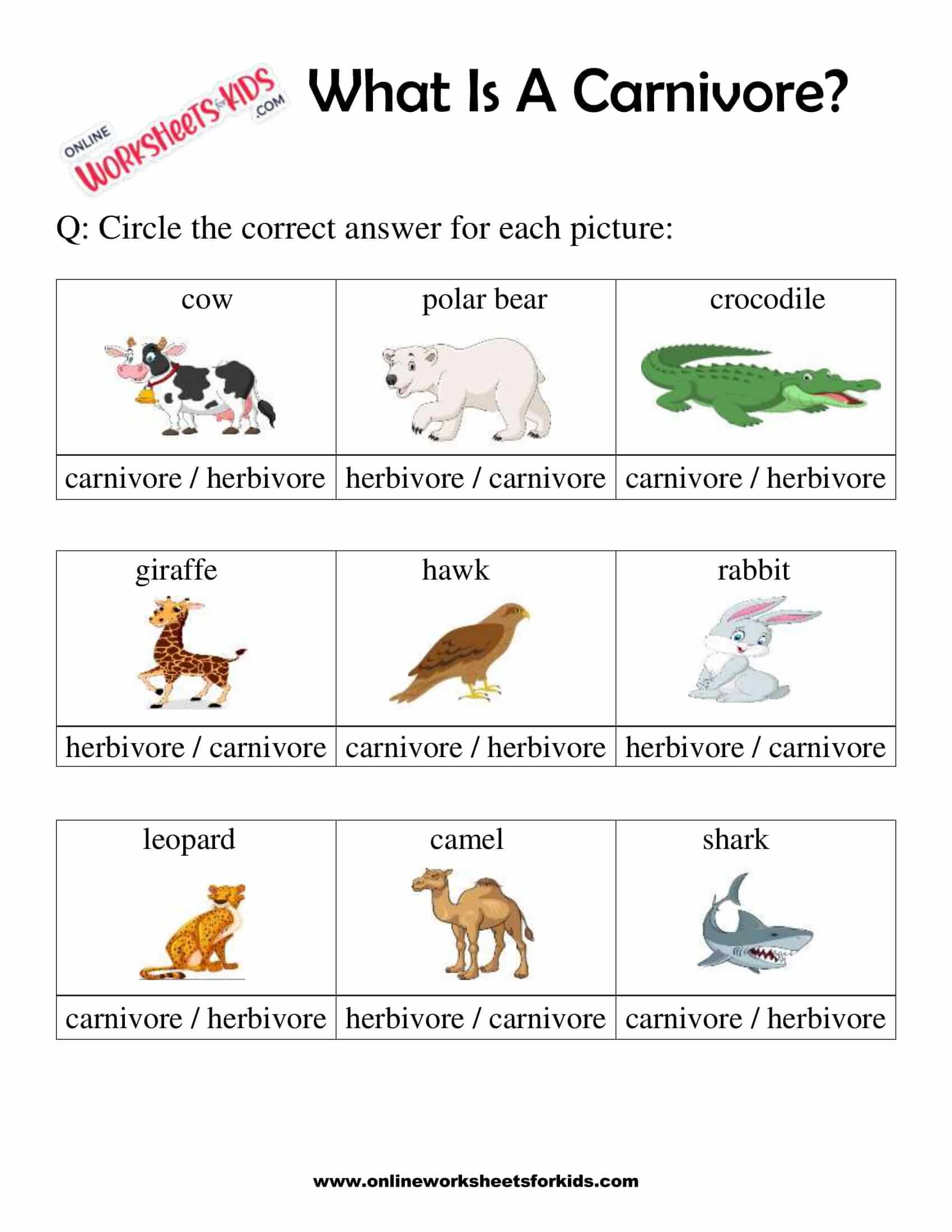
The vast savannas, stretching across Africa and other continents, are home to a diverse array of bird species, each with unique dietary habits. Understanding whether savanna birds are carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores is crucial for bird enthusiasts, researchers, and conservationists alike. This blog explores the feeding behaviors of these fascinating creatures, shedding light on their roles in the ecosystem and how they adapt to their environments. (savanna birds, bird diets, ecosystem roles)
Carnivorous Savanna Birds: The Hunters
Carnivorous birds in the savanna are skilled predators, primarily feeding on small mammals, reptiles, and other birds. Eagles, hawks, and owls are prime examples, utilizing their sharp talons and keen eyesight to hunt. These birds play a vital role in controlling prey populations, maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. (carnivorous birds, predators, ecosystem balance)
Key Carnivorous Species
- Secretary Bird: Known for its distinctive appearance and ability to hunt snakes.
- Martial Eagle: One of Africa’s largest eagles, preying on small antelopes and monkeys.
- Barn Owl: A nocturnal hunter specializing in rodents.
📌 Note: Carnivorous birds often have hooked beaks and powerful talons adapted for tearing flesh.
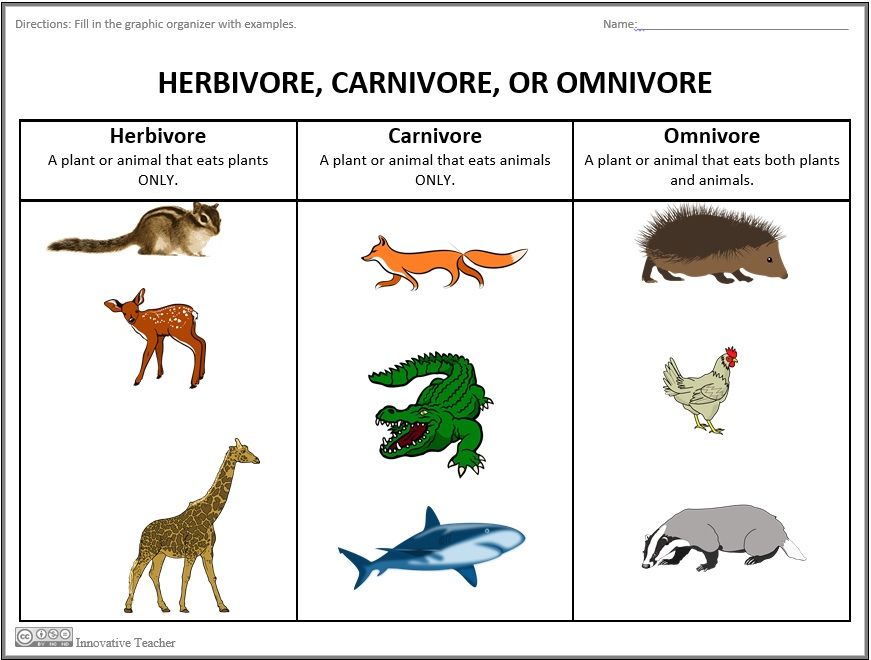
Herbivorous Savanna Birds: The Grazers

While less common, some savanna birds are primarily herbivores, feeding on seeds, fruits, and vegetation. These birds contribute to seed dispersal and plant pollination, supporting the savanna’s flora. (herbivorous birds, seed dispersal, plant pollination)
Notable Herbivorous Species
- Ostrich: The world’s largest bird, feeding on plants and occasionally insects.
- Weaver Birds: Known for their intricate nests and diet of seeds and grains.
- Hornbills: Consume fruits and play a role in forest regeneration.
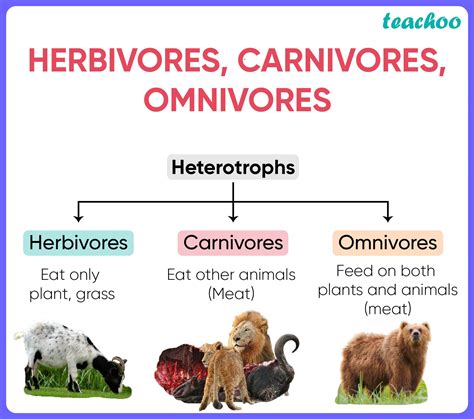
Omnivorous Savanna Birds: The Adaptable Eaters

Many savanna birds are omnivores, displaying remarkable dietary flexibility. They consume a mix of plant matter, insects, and small animals, allowing them to thrive in diverse environments. (omnivorous birds, dietary flexibility, adaptable eaters)
Prominent Omnivorous Species
- Crows: Highly intelligent, feeding on almost anything available.
- Guinea Fowl: Forage for seeds, insects, and small reptiles.
- Hoopoe: Known for their long bills, they eat insects and berries.
| Diet Type | Examples | Ecosystem Role |
|---|---|---|
| Carnivorous | Eagle, Owl, Secretary Bird | Predators, control prey populations |
| Herbivorous | Ostrich, Weaver Bird, Hornbill | Seed dispersers, pollinators |
| Omnivorous | Crow, Guinea Fowl, Hoopoe | Adaptable, contribute to multiple roles |
Checklist: Identifying Bird Diets
- Beak Shape: Hooked beaks often indicate carnivores, while flat beaks suggest herbivores.
- Feeding Behavior: Observe hunting vs. foraging activities.
- Habitat: Carnivores often perch high for hunting, while herbivores stay close to vegetation.
Savanna birds exhibit a wide range of dietary preferences, from strict carnivores to adaptable omnivores. Understanding their feeding habits not only enriches our knowledge but also highlights their importance in maintaining ecological balance. Whether you’re a birdwatcher or a conservationist, appreciating these differences can deepen your connection to the natural world. (birdwatching, conservation, ecological balance)
What is the most common diet type among savanna birds?
+Omnivorous diets are most common, as they allow birds to adapt to varying food availability in the savanna.
How do carnivorous birds contribute to the ecosystem?
+Carnivorous birds control prey populations, preventing overgrazing and maintaining biodiversity.
Can herbivorous birds survive without plants?
+No, herbivorous birds rely on plants for food and cannot survive without them.



