The Nucleus: Why Remembering Its Role Matters
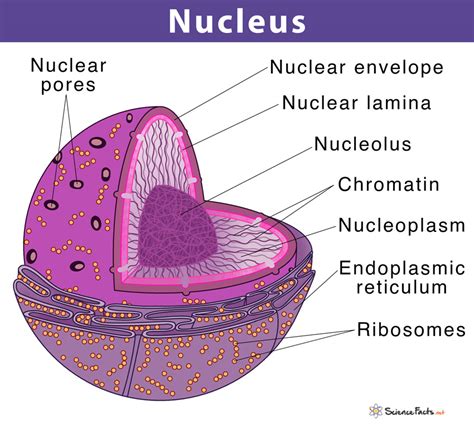
The nucleus, often referred to as the “control center” of the cell, plays a pivotal role in maintaining cellular functions and ensuring the continuity of life. Understanding its significance is crucial, whether you’re a student, a researcher, or simply curious about biology. This post delves into the nucleus’s role, its importance, and why remembering its functions matters in various contexts, including education, research, and health. (cell biology, nuclear function, genetic material)
What is the Nucleus and Why Does It Matter?
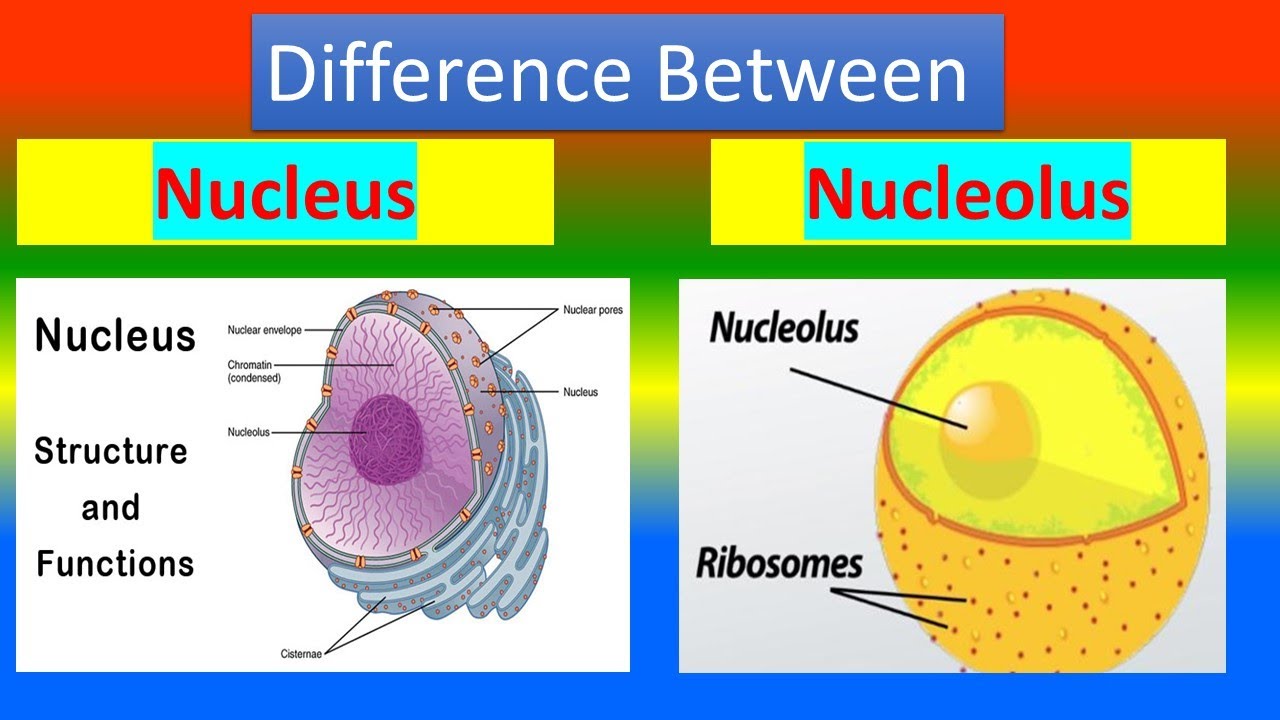
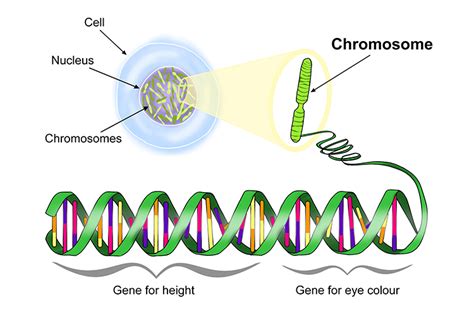
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells, housing the cell’s genetic material, DNA. It acts as the cell’s command center, regulating gene expression and overseeing cellular activities. Without the nucleus, cells would lack direction, leading to chaos in biological processes. (eukaryotic cells, DNA, gene expression)
Key Functions of the Nucleus
- Genetic Information Storage: The nucleus stores DNA, the blueprint of life, ensuring accurate transmission of traits from one generation to the next.
- Protein Synthesis Regulation: It controls the synthesis of proteins by transcribing DNA into RNA, a process vital for cell growth and repair.
- Cell Cycle Control: The nucleus regulates the cell cycle, ensuring proper division and preventing abnormalities like cancer.
📌 Note: The nucleus is not present in prokaryotic cells, which rely on a nucleoid region for DNA storage.
The Nucleus in Education and Research
In educational settings, understanding the nucleus is fundamental to grasping advanced biological concepts. It serves as a foundation for topics like genetics, molecular biology, and biotechnology. Researchers rely on nuclear studies to develop treatments for genetic disorders and cancers, highlighting its commercial relevance in the healthcare industry. (genetics, molecular biology, biotechnology)
Practical Applications of Nuclear Knowledge
- Genetic Engineering: Manipulating nuclear DNA allows scientists to create genetically modified organisms (GMOs) for agriculture and medicine.
- Cancer Research: Understanding nuclear abnormalities helps in developing targeted therapies for cancer.
- Forensic Science: Nuclear DNA analysis is crucial for identifying individuals in criminal investigations.
How to Remember the Nucleus’s Role
To reinforce your understanding, use mnemonic devices or visual aids. For instance, associate the nucleus with a “library” that stores and manages genetic “books.” Below is a checklist to help you retain key points:
- [ ] Identify the nucleus as the cell’s control center.
- [ ] Understand its role in storing and transmitting genetic information.
- [ ] Recognize its importance in protein synthesis and cell cycle regulation.
- [ ] Explore its applications in research and healthcare.
Final Thoughts
The nucleus is more than just a cellular component; it’s the cornerstone of life’s continuity and diversity. Whether you’re studying biology, working in research, or simply curious about how cells function, remembering the nucleus’s role is essential. Its significance spans educational, scientific, and commercial domains, making it a topic worth exploring further. (cellular biology, genetic research, healthcare advancements)
What is the primary function of the nucleus?
+
The nucleus primarily stores and protects genetic material (DNA) and regulates gene expression, ensuring proper cell function.
Can cells survive without a nucleus?
+
Eukaryotic cells cannot survive without a nucleus, as it is essential for DNA storage and cellular regulation. Prokaryotic cells, however, lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region for DNA.
How does the nucleus contribute to cancer research?
+
The nucleus plays a key role in cancer research by helping scientists understand how abnormalities in DNA and cell cycle regulation lead to cancer, enabling the development of targeted therapies.



